Downregulation of c-Jun expression by transcription factor C/EBPalpha is critical for granulocytic lineage commitment
- PMID: 12446786
- PMCID: PMC139872
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.24.8681-8694.2002
Downregulation of c-Jun expression by transcription factor C/EBPalpha is critical for granulocytic lineage commitment
Abstract
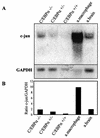
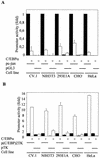
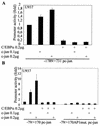
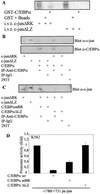
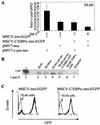
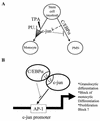
The transcription factor C/EBPalpha is crucial for the differentiation of granulocytes. Conditional expression of C/EBPalpha triggers neutrophilic differentiation, and C/EBPalpha can block 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced monocytic differentiation of bipotential myeloid cells. In C/EBPalpha knockout mice, no mature granulocytes are present. A dramatic increase of c-Jun mRNA in C/EBPalpha knockout mouse fetal liver was observed. c-Jun, a component of the AP-1 transcription factor complex and a coactivator of the transcription factor PU.1, is important for monocytic differentiation. Here we report that C/EBPalpha downregulates c-Jun expression to drive granulocytic differentiation. An ectopic increase of C/EBPalpha expression decreases the c-Jun mRNA level, and the human c-Jun promoter activity is downregulated eightfold in the presence of C/EBPalpha. C/EBPalpha and c-Jun interact through their leucine zipper domains, and this interaction prevents c-Jun from binding to DNA. This results in downregulation of c-Jun's capacity to autoregulate its own promoter through the proximal AP-1 site. Overexpression of c-Jun prevents C/EBPalpha-induced granulocytic differentiation. Thus, we propose a model in which C/EBPalpha needs to downregulate c-Jun expression and transactivation capacity for promoting granulocytic differentiation.
Figures



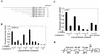







References
-
- Angel, P., K. Hattori, T. Smeal, and M. Karin. 1988. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell 55:875-885. - PubMed
-
- Angel, P., E. A. Allgretto, St. T. Okino, K. Hattori, W. J. Boyle, T. Hunter, and M. Karin. 1988. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature 332:166-171. - PubMed
-
- Behre, G., L. T. Smith, and D. G. Tenen. 1999. Use of a promoterless Renilla luciferase vector as an internal control plasmid for transient co-transfection assays of Ras-mediated transcription activation. BioTechniques 26:24-26. - PubMed
-
- Behre, G., P. Zhang, D. E. Zhang, and D. G. Tenen. 1999. Analysis of the modulation of transcriptional activity in myelopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Methods 17:231-237. - PubMed
-
- Behre, G., A. J. Whitmarsh, M. P. Coghlan, T. Hoang, C. L. Carpenter, D. E. Zhang, R. J. Davis, and D. G. Tenen. 1999. c-jun is a JNK-independent coactivator of the PU.1 transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 274:4939-4946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
