CYR61 (CCN1) is essential for placental development and vascular integrity
- PMID: 12446788
- PMCID: PMC139880
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.24.8709-8720.2002
CYR61 (CCN1) is essential for placental development and vascular integrity
Abstract
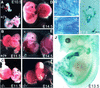
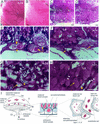
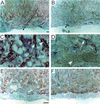
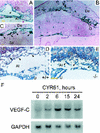
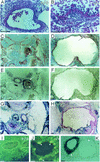
CYR61 (CCN1) is a member of the CCN family of secreted matricellular proteins that includes connective tissue growth factor (CCN2), NOV (CCN3), WISP-1 (CCN4), WISP-2 (CCN5), and WISP-3 (CCN6). First identified as the product of a growth factor-inducible immediate-early gene, CYR61 is an extracellular matrix-associated angiogenic inducer that functions as a ligand of integrin receptors to promote cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation. Aberrant expression of Cyr61 is associated with breast cancer, wound healing, and vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and restenosis. To understand the functions of CYR61 during development, we have disrupted the Cyr61 gene in mice. We show here that Cyr61-null mice suffer embryonic death: approximately 30% succumbed to a failure in chorioallantoic fusion, and the reminder perished due to placental vascular insufficiency and compromised vessel integrity. These findings establish CYR61 as a novel and essential regulator of vascular development. CYR61 deficiency results in a specific defect in vessel bifurcation (nonsprouting angiogenesis) at the chorioallantoic junction, leading to an undervascularization of the placenta without affecting differentiation of the labyrinthine syncytiotrophoblasts. This unique phenotype is correlated with impaired Vegf-C expression in the allantoic mesoderm, suggesting that CYR61-regulated expression of Vegf-C plays a role in vessel bifurcation. The genetic and molecular basis of vessel bifurcation is presently unknown, and these findings provide new insight into this aspect of angiogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pro-angiogenic activities of CYR61 (CCN1) mediated through integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha6beta1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 29;277(48):46248-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209288200. Epub 2002 Oct 2. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12364323
-
Regulation of angiogenesis and endothelial cell function by connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and cysteine-rich 61 (CYR61).Angiogenesis. 2002;5(3):153-65. doi: 10.1023/a:1023823803510. Angiogenesis. 2002. PMID: 12831056
-
The angiogenic factor Cyr61 activates a genetic program for wound healing in human skin fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2001 Dec 14;276(50):47329-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107666200. Epub 2001 Oct 2. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11584015
-
The CCN family: a new stimulus package.J Endocrinol. 2003 Aug;178(2):169-75. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1780169. J Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12904165 Review.
-
Role of CCN, a vertebrate specific gene family, in development.Dev Growth Differ. 2009 Jan;51(1):55-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2009.01077.x. Dev Growth Differ. 2009. PMID: 19128405 Review.
Cited by
-
Matricellular protein CCN1 promotes regression of liver fibrosis through induction of cellular senescence in hepatic myofibroblasts.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 May;33(10):2078-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00049-13. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23508104 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Matrix Proteins in Cardiac Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1338. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031338. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
O-fucosylation of thrombospondin type 1 repeats is essential for ECM remodeling and signaling during bone development.Matrix Biol. 2022 Mar;107:77-96. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2022.02.002. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Matrix Biol. 2022. PMID: 35167946 Free PMC article.
-
CCN1 interacts with integrins to regulate intestinal stem cell proliferation and differentiation.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 3;13(1):3117. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30851-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35660741 Free PMC article.
-
Prdm6 is essential for cardiovascular development in vivo.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 21;8(11):e81833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081833. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anson-Cartwright, L., K. Dawson, D. Holmyard, S. J. Fisher, R. A. Lazzarini, and J. C. Cross. 2000. The glial cells missing-1 protein is essential for branching morphogenesis in the chorioallantoic placenta. Nat. Genet. 25:311-314. - PubMed
-
- Bader, B. L., H. Rayburn, D. Crowley, and R. O. Hynes. 1998. Extensive vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and organogenesis precede lethality in mice lacking all alpha v integrins. Cell 95:507-519. - PubMed
-
- Bork, P. 1993. The modular architecture of a new family of growth regulators related to connective tissue growth factor. FEBS Lett. 327:125-130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
