Effects of dietary fat source and subtherapeutic levels of antibiotic on the bacterial community in the ileum of broiler chickens at various ages
- PMID: 12450811
- PMCID: PMC134372
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.12.5918-5924.2002
Effects of dietary fat source and subtherapeutic levels of antibiotic on the bacterial community in the ileum of broiler chickens at various ages
Abstract
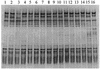
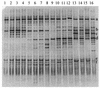
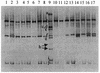
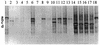
The effect of dietary fat source (soy oil or a mixture of lard and tallow) and dietary supplementation with antibiotics (a combination of avilamycin at 10 mg kg of feed(-1) and salinomycin at 40 mg kg of feed(-1)) on the bacterial community in the ileum of broiler chickens at different ages (7, 14, 21, and 35 days) was studied using PCR with denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis and bacteriological culture. The bacterial origin of fragments in DGGE profiles was identified by sequencing. Bacterial enumeration results, together with PCR-DGGE profiles, showed that the composition of the microflora was age dependent and influenced by dietary fat source and antibiotic supplementation. An increased incidence of streptococci, enterobacteria, and Clostridium perfringens with age of the chickens was demonstrated. Lactobacilli and C. perfringens were the bacterial groups most strongly affected by the dietary treatments. Moreover, different strains (clonal variants of the alpha-toxin gene) of C. perfringens type A were detected in response to age, dietary fat source, and dietary supplementation with antibiotics.
Figures
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, E. M., G. C. Mead, and D. A. Barnum. 1972. The intestinal flora of the chicken in the period 2 to 6 weeks of age, with particular reference to the anaerobic bacteria. Br. Poult. Sci. 13:311-326. - PubMed
-
- Coates, M. E., R. Fuller, G. F. Harrison, M. Lev, and S. F. Suffolk. 1963. A comparison of the growth of chicks in the Gustafsson germ-free apparatus and in a conventional environment with and without dietary supplement of penicillin. Br. J. Nutr. 17:141-150. - PubMed
-
- Cole, C. B., and R. Fuller. 1984. Bile acid deconjugation and attachment of chicken gut bacteria: their possible role in growth depression. Br. Poult. Sci. 25:227-231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

