Construction and evaluation of plasmid vectors optimized for constitutive and regulated gene expression in Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates
- PMID: 12450816
- PMCID: PMC134411
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.12.5956-5964.2002
Construction and evaluation of plasmid vectors optimized for constitutive and regulated gene expression in Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates
Abstract
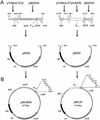
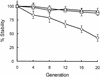
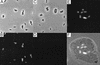
Genetic studies with Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates are hampered by the limited availability of cloning vectors and by the inherent resistance of these isolates to the most common antibiotics used for genetic selection. Also, some of the promoters widely employed for gene expression in Escherichia coli are inefficient in B. cepacia. In this study, we have utilized the backbone of the vector pME6000, a derivative of the pBBR1 plasmid that was originally isolated from Bordetella bronchiseptica, to construct a set of vectors useful for gene expression in B. cepacia. These vectors contain either the constitutive promoter of the S7 ribosomal protein gene from Burkholderia sp. strain LB400 or the arabinose-inducible P(BAD) promoter from E. coli. Promoter sequences were placed immediately upstream of multiple cloning sites in combination with the minimal sequence of pME6000 required for plasmid maintenance and mobilization. The functionality of both vectors was assessed by cloning the enhanced green fluorescent protein gene (e-gfp) and determining the levels of enhanced green fluorescent protein expression and fluorescence emission for a variety of clinical and environmental isolates of the B. cepacia complex. We also demonstrate that B. cepacia carrying these constructs can readily be detected intracellularly by fluorescence microscopy following the infection of Acanthamoeba polyphaga.
Figures

References
-
- Abe, M., M. Tsuda, M. Kimoto, S. Inouye, A. Nakazawa, and T. Nakazawa. 1996. A genetic analysis system of Burkholderia cepacia: construction of mobilizable transposons and a cloning vector. Gene 174:191-194. - PubMed
-
- Amer, A. O., and M. A. Valvano. 2002. Conserved aspartic acids are essential for the enzymatic activity of the WecA protein initiating the biosynthesis of O-specific lipopolysaccharide and enterobacterial common antigen in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 148:571-582. - PubMed
-
- Antoine, R., and C. Locht. 1992. Isolation and molecular characterization of a novel broad-host-range plasmid from Bordetella bronchiseptica with sequence similarities to plasmids from gram-positive organisms. Mol. Microbiol. 6:1785-1799. - PubMed
-
- Bevivino, A., C. Dalmastri, S. Tabacchioni, L. Chiarini, M. L. Belli, S. Piana, A. Materazzo, P. Vandamme, and G. Manno. 2002. Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria from clinical and environmental sources in Italy: genomovar status and distribution of traits related to virulence and transmissibility. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:846-851. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bevivino, A., S. Sarrocco, C. Dalmastri, S. Tabacchioni, C. Cantale, and L. Chiarini. 1998. Characterization of a free-living maize-rhizosphere population of Burkholderia cepacia: effect of seed treatment on disease suppression and growth promotion in maize. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 27:225-237.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

