Rapid identification, differentiation, and proposed new taxonomic classification of Bifidobacterium lactis
- PMID: 12450873
- PMCID: PMC134397
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.12.6429-6434.2002
Rapid identification, differentiation, and proposed new taxonomic classification of Bifidobacterium lactis
Abstract
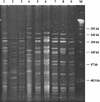
Identification of Bifidobacterium lactis and Bifidobacterium animalis is problematic because of phenotypic and genetic homogeneities and has raised the question of whether they belong to one unique taxon. Analysis of the 16S-23S internally transcribed spacer region of B. lactis DSM10140(T), B. animalis ATCC 25527(T), and six potential B. lactis strains suggested two distinct clusters. Two specific 16S-23S spacer rRNA gene-targeted primers have been developed for specific detection of B. animalis. All of the molecular techniques used (B. lactis or B. animalis PCR primers, enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus PCR) demonstrated that B. lactis and B. animalis form two main groups and suggest a revision of the strains assigned to B. animalis. We propose that B. lactis should be separated from B. animalis at the subspecies level.
Figures




References
-
- Bourget, N. L., H. Philippe, I. Mangin, and B. Decaris. 1996. 16S rRNA and 16S to 23S internal transcribed spacer sequence analyses reveal inter- and intraspecific Bifidobacterium phylogeny. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46:102-111. - PubMed
-
- Cai, Y., M. Matsumoto, and Y. Benno. 2000. Bifidobacterium lactis Meile et al. 1997 is a subjective synonym of Bifidobacterium animalis (Mitsuoka 1969) Scardovi and Trovatelli 1974. Microbiol. Immunol. 44:815-820. - PubMed
-
- Jian, W., L. Zhu, and X. Dong. 2001. New approach to phylogenetic analysis of the genus Bifidobacterium based on partial HSP60 gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:1633-1638. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

