Phylogenetic analysis of acute bee paralysis virus strains
- PMID: 12450876
- PMCID: PMC134446
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.12.6446-6450.2002
Phylogenetic analysis of acute bee paralysis virus strains
Abstract
Reverse transcription-PCR assays have been established for a quick, sensitive, and specific diagnosis of acute bee paralysis virus (ABPV), a common virus of the honeybee (Apis mellifera), directly from clinical samples. A 3,071-nucleotide fragment of the ABPV genome, which includes the entire capsid polyprotein gene, was amplified from Austrian, German, Polish, and Hungarian ABPV samples and sequenced, and the sequences were compared. The alignment of a smaller fragment with ABPV sequences from the United States and the United Kingdom revealed nucleotide identity rates between 89 and 96%, respectively. Phylogenetic trees which display the molecular relationship between the viruses of different geographic origin were constructed.
Figures
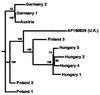
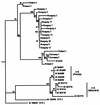
References
-
- Allen, M., and B. Ball. 1996. The incidence and world distribution of the honey bee viruses. Bee World 77:141-162.
-
- Allen, M. F., and B. V. Ball. 1995. Characterisation and serological relationships of strains of Kashmir bee virus. Ann. Appl. Biol. 126:471-484.
-
- Bailey, L., A. J. Gibbs, and R. D. Woods. 1963. Two viruses from adult honey bees (Apis mellifera Linnaeus). Virology 21:390-395. - PubMed
-
- Ball, B. V. 1997. Varroa and viruses, p. 11-15. In P. Munn and R. Jones (ed.), Varroa! Fight the mite. International Bee Research Association, Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom.
-
- Ball, B. V., and M. F. Allen. 1988. The prevalence of pathogens in the honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies infested with the parasitic mite Varroa jacobsoni. Ann. Appl. Biol. 113:237-244.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

