Glia induce dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons by modulating the balance between bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and BMP antagonists
- PMID: 12451137
- PMCID: PMC6758753
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-23-10377.2002
Glia induce dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons by modulating the balance between bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and BMP antagonists
Abstract
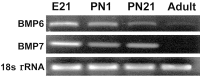
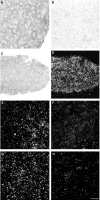
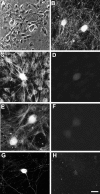
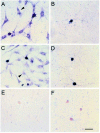
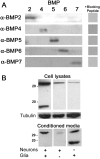
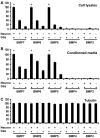
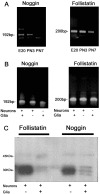
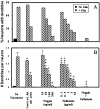
Dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons requires specific trophic interactions. Previous studies have demonstrated that either coculture with glia or exposure to recombinant bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) is both necessary and sufficient to induce dendrite formation. These observations led us to test the hypothesis that BMPs mediate glial-induced dendritic growth. In situ hybridization and immunocytochemical studies indicate that the spatiotemporal expression of BMP5, -6, and -7 in rat superior cervical ganglia (SCG) is consistent with their proposed role in dendritogenesis. In vitro, both SCG glia and neurons were found to express BMP mRNA and protein when grown in the presence or absence of the other cell type. However, addition of ganglionic glia to cultured sympathetic neurons causes a marked increase in BMP proteins coincident with a significant decrease in follistatin and noggin. Functional assays indicate that glial-induced dendritic growth is significantly reduced by BMP7 antibodies and completely inhibited by exogenous noggin and follistatin. These data suggest that glia influence the rapid perinatal expansion of the dendritic arbor in sympathetic neurons by increasing BMP activity via modulation of the balance between BMPs and their antagonists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-5 (BMP-5) promotes dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons.BMC Neurosci. 2001;2:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-2-12. Epub 2001 Sep 11. BMC Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11580864 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -4 limit the number of enteric neurons but promote development of a TrkC-expressing neurotrophin-3-dependent subset.J Neurosci. 2004 Apr 28;24(17):4266-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3688-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15115823 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species are involved in BMP-induced dendritic growth in cultured rat sympathetic neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jul;67:116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.06.007. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26079955 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism for the action of bone morphogenetic proteins and regulation of their activity.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002 Aug 15;27(16 Suppl 1):S10-5. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200208151-00004. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002. PMID: 12205413 Review.
-
The dynamic role of bone morphogenetic proteins in neural stem cell fate and maturation.Dev Neurobiol. 2012 Jul;72(7):1068-84. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22022. Dev Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22489086 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
REST and CoREST modulate neuronal subtype specification, maturation and maintenance.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 7;4(12):e7936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007936. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19997604 Free PMC article.
-
The sympathetic nervous system in development and disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021 Nov;22(11):685-702. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00523-y. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34599308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meningeal Bmps Regulate Cortical Layer Formation.Brain Plast. 2018 Dec 26;4(2):169-183. doi: 10.3233/BPL-170048. Brain Plast. 2018. PMID: 30598868 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between fibroblast growth factor and bone morphogenetic proteins regulates gap junction-mediated intercellular communication in lens cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jun;19(6):2631-41. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-02-0124. Epub 2008 Apr 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18400943 Free PMC article.
-
Glia determine the course of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated dendritogenesis and provide a soluble inhibitory cue to dendritic growth in the brainstem.Neuroscience. 2012 Apr 5;207:333-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.01.013. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22306205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ai X, Cappuzzello J, Hall AK. Activin and bone morphogenetic proteins induce calcitonin gene-related peptide in embryonic sensory neurons in vitro. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1999;14:506–518. - PubMed
-
- Barres BA. A new role for glia: generation of neurons! Cell. 1999;97:667–670. - PubMed
-
- Bruckenstein DA, Higgins D. Morphological differentiation of embryonic rat sympathetic neurons in tissue culture. I. Conditions under which neurons form axons but not dendrites. Dev Biol. 1988;128:324–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
