Involvement of CD27/CD70 interactions in antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activity by perforin-mediated cytotoxicity
- PMID: 12452832
- PMCID: PMC1906551
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.02012.x
Involvement of CD27/CD70 interactions in antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activity by perforin-mediated cytotoxicity
Abstract
CD27 molecules are shown to be essential in the regulation of the death, activation and differentiation of T and B cells. However, the influence of CD27 on cytotoxic T-cell function remains obscure. Autologous EBV transformed B-cell lines (LCL), which highly express CD27 ligand CD70, here stimulated T cells and induced the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) activity via T-cell antigen receptors (TCR). The cytotoxicity against LCL was diminished when anti-CD70 blocking MoAb was added initially in the culture. Resting T cells killed more CD70-transfected P815 cells than wild type P815 cells in the presence of anti-CD3 MoAb as measured by a 4-h 51Cr release assay, and the cytotoxicity of both of the cell populations completely disappeared in the presence of concanamycin A (CMA). The expression of the perforin by the LCL-induced CTL in the presence of anti-CD70 blocking MoAb was diminished as compared with that without the blockage of CD27/CD70 interactions. The CTL induced by LCL did not kill Fas-transfected WR cells. CD27 signalling in the T cells did not affect Fas ligand (FasL) mRNA expression, LAK activity and IFN-gamma synthesis in humans. Our data demonstrate that CD27/CD70 interactions enhance the cytotoxicity of CTL in the induction phase through enhancement of killing activity induced via the perforin-dependent mechanism, but not via the Fas/FasL system.
Figures
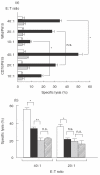
 anti-CD3MoAb + CMA. (b) Effects of CD27/CD70 interactions on cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity. E+ cells (2 × 106/well) were cocultured with autologous LCL (8 × 105/well) in the presence (▪,
anti-CD3MoAb + CMA. (b) Effects of CD27/CD70 interactions on cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity. E+ cells (2 × 106/well) were cocultured with autologous LCL (8 × 105/well) in the presence (▪,  ) of 5 µg/ml anti-CD70 MoAb or in the absence (□,
) of 5 µg/ml anti-CD70 MoAb or in the absence (□,  ) of anti-CD70 MoAb for 12 days. The pretreated cells were tested for the cytotoxicity against autologous LCL (1 × 104/well) at E : T ratios of 40 : 1 and 20 : 1 with (
) of anti-CD70 MoAb for 12 days. The pretreated cells were tested for the cytotoxicity against autologous LCL (1 × 104/well) at E : T ratios of 40 : 1 and 20 : 1 with ( ,
,  ) or without (□, ▪) CMA (1000 n
) or without (□, ▪) CMA (1000 n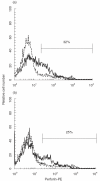
 ) and LCL (
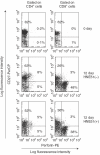
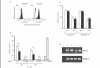
) and LCL ( ) were mixed with anti-Fas MoAb (7C11) which induced apotosis of the Fas-expressing cells in a 12- h 51Cr-release assay for positive controls. Results are expressed as the mean percentage of cytotoxicity ± SD of triplicates. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (c) IL-2 (25 ng/ml) activated E+ cells (2 × 106/well) were cocultured with mock/300–19 or CD70/300–19 (8 × 105/well) in the absence (□) of anti-CD70 MoAb or in the presence (▪) for 5 days. The pretreated cells were tested for the cytotoxicity against Fas/WR at E : T ratios of 40 : 1 and 20 : 1 in a 12-h 51Cr-release assay. Results are expressed as the mean percentage of cytotoxicity ± SD of triplicates. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (d) The expression of FasL and β2-microglobulin were analysed by RT-PCR as described in the Materials and Methods. Lane 1: no DNA, lane 2 : 24 h IL-2 activated E+ cells with mock/300–19, lane 3 : 48 h IL-2 activated E+ cells with mock/300–19, lane 4 : 24 h IL-2 activated E+ cells with CD70/300–19, and lane 5 : 48 h IL-2 activated E+ cells with CD70/300–19. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. Statistical analysis: two-sample t-test; n.s., not significant; *P < 0·01.
) were mixed with anti-Fas MoAb (7C11) which induced apotosis of the Fas-expressing cells in a 12- h 51Cr-release assay for positive controls. Results are expressed as the mean percentage of cytotoxicity ± SD of triplicates. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (c) IL-2 (25 ng/ml) activated E+ cells (2 × 106/well) were cocultured with mock/300–19 or CD70/300–19 (8 × 105/well) in the absence (□) of anti-CD70 MoAb or in the presence (▪) for 5 days. The pretreated cells were tested for the cytotoxicity against Fas/WR at E : T ratios of 40 : 1 and 20 : 1 in a 12-h 51Cr-release assay. Results are expressed as the mean percentage of cytotoxicity ± SD of triplicates. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (d) The expression of FasL and β2-microglobulin were analysed by RT-PCR as described in the Materials and Methods. Lane 1: no DNA, lane 2 : 24 h IL-2 activated E+ cells with mock/300–19, lane 3 : 48 h IL-2 activated E+ cells with mock/300–19, lane 4 : 24 h IL-2 activated E+ cells with CD70/300–19, and lane 5 : 48 h IL-2 activated E+ cells with CD70/300–19. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. Statistical analysis: two-sample t-test; n.s., not significant; *P < 0·01.References
-
- Gustafsson A, Levitsky V, Zou JZ, et al. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) load in bone marrow transplant recipients at risk to develop posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease. prophylactic infusion of EBV-specific cytotoxic T cells. Blood. 2000;95:807–14. - PubMed
-
- Lowin B, Hahne M, Mattmann C, Tschopp J. Cytolytic T-cell cytotoxicity is mediated through perforin and Fas lytic pathways. Nature. 1994;370:650–2. - PubMed
-
- Kagi D, Vignaux F, Ledermann B, Burki K, Depraetere V, Nagata S, Hengartner H, Golstein P. Fas and perforin pathways as major mechanisms of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Science. 1994;265:528–30. - PubMed
-
- Berke G. The CTL's kiss of death. Cell. 1995;81:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Schroter M, Lowin B, Borner C, Tschopp J. Regulation of Fas (Apo-1/CD95)- and perforin-mediated lytic pathways of primary cytotoxic T lymphocytes by the protooncogene bcl-2. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:3509–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

