Normalized quantification of human cytomegalovirus DNA by competitive real-time PCR on the LightCycler instrument
- PMID: 12454150
- PMCID: PMC154596
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.12.4547-4553.2002
Normalized quantification of human cytomegalovirus DNA by competitive real-time PCR on the LightCycler instrument
Abstract
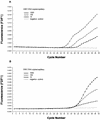
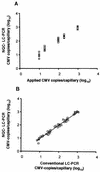
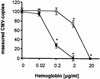
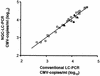
The development of a novel normalized quantitative competitive real-time PCR on the LightCycler instrument (NQC-LC-PCR) and its application to the quantification of cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA in clinical samples are described. A heterologous competitor DNA was spiked into test samples and served as an internal amplification control. The internal control (IC) DNA in the test samples was coamplified with the CMV DNA and was tested against a calibrator sample that contained equal amounts of IC DNA and CMV reference standard DNA. An algorithm was developed to normalize possible varying amplification efficiencies between the standard and the samples. After normalization, CMV DNA copy numbers were determined in absolute terms. In a routine clinical setting, normalized quantification by NQC-LC-PCR using a single IC concentration led to results ranging from 500 to 50,000 CMV DNA copies/ml. The results obtained with conventional real-time quantification on the LightCycler instrument were almost identical to those obtained with the NQC-LC-PCR-based quantification. This was the case only for samples in which the PCR was not inhibited. With partially inhibited samples, NQC-LC-PCR was still able to correctly quantify CMV DNA copy numbers even when the PCR was inhibited by about 70%. By analyzing 80 undefined clinical samples, we found that NQC-LC-PCR was suitable for the routine assessment of CMV DNA in clinical plasma samples. Since the ICs were already added to the samples during the DNA purification, almost the entire assay was controlled for sample adequacy. Thus, false negative results were precluded. The NQC-LC-PCR approach developed should be adaptable for additional microbiological applications.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Robaiy, S., S. Rupf, and K. Eschrich. 2001. Rapid competitive PCR using melting curve analysis for DNA quantification. BioTechniques 31:1382-1388. - PubMed
-
- Bai, X., B. B. Rogers, P. C. Harkins, J. Sommerauer, R. Squires, K. Rotondo, A. Quan, D. B. Dawson, and R. H. Scheuermann. 2000. Predictive value of quantification PCR-based viral burden analysis for eight human herpesviruses in pediatric solid organ transplant patients. J. Mol. Diagn. 2:191-201. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benedetti, E., M. Mihalov, M. Asolati, J. Kirby. T. Dunn, V. Raofi, M. Fontane, and R. Pollak. 1998. A prospective study of the predictive value of polymerase chain reaction assay for cytomegalovirus in asymptomatic kidney transplant recipients. Clin. Transplant. 12:391-395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

