Evaluation of a new rapid test for the combined detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and hepatitis B virus e antigen
- PMID: 12454159
- PMCID: PMC154615
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.12.4603-4606.2002
Evaluation of a new rapid test for the combined detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and hepatitis B virus e antigen
Abstract
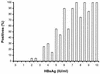
There are about 350 million chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) carriers worldwide. A proactive approach to the management of this disease is likely to reduce the morbidity and mortality caused by HBV. This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of a novel tool for discriminating between infected and noninfected subjects, the hepatitis B sAg/eAg test (Binax Inc., Portland, Maine). The test is designed to rapidly and accurately detect both the HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) and the HBV e antigen (HBeAg). A cohort of 942 subjects was tested. The serum clinical sensitivity of the hepatitis B sAg/eAg test was 99.75 and 96.37% for HBsAg and HBeAg, respectively. Serum clinical specificity was 99.32% for HBsAg and 98.99% for HBeAg. Analytical sensitivity was satisfactory for the purposes of population screening. Visual evaluation showed that the test signals were stable for at least 3 h after the recommended evaluation time. No interference or cross-reactivity was observed with known interfering substances and virologic markers. These results indicate that the hepatitis B sAg/eAg test is well suited to the accurate detection of HBV carriers. In addition to the good clinical specificity and sensitivity of this test, its stability and user-friendly design mean that a correct performance, even under field conditions, is highly likely. Consequently, the hepatitis B sAg/eAg test has the potential to identify subjects who require HBV vaccination (HBsAg(-) and HBeAg(-)) and HBV-infected individuals who might benefit most from antiviral therapy (HBsAg(+) and HBeAg(+)).
Figures
References
-
- Ganem, D., and R. J. Schneider. 2001. Hepadnaviridae and their replication, p. 2703-2737. In D. M. Knipe, P. M. Howley, R. M. Chanook, T. P. Monath, B. Roizman, and S. E. Straus (ed.), Fields virology, 4th ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, Pa.
-
- Hollinger, F. B., and T. J. Liang. 2001. Hepatitis B virus, p. 2971-3036. In D. M. Knipe, P. M. Howley, R. M. Chanook, T. P. Monath, B. Roizman, and S. E. Straus (ed.), Fields virology, 4th ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, Pa.
-
- Lee, W. 1997. Hepatitis B virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 337:1733-1745. - PubMed
-
- McMahon, B. J. 1997. Hepatocellular carcinoma and viral hepatitis, p. 315-330. In R. A. Wilson (ed.), Viral hepatitis. Marcel Dekker, New York, N.Y.
-
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2000. User protocol for evaluation of qualitative test performance; proposed guideline EP12-P, vol. 20, no. 15. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Pa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources