Intense inflammation in bladder carcinoma is associated with angiogenesis and indicates good prognosis
- PMID: 12454772
- PMCID: PMC2376289
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600615
Intense inflammation in bladder carcinoma is associated with angiogenesis and indicates good prognosis
Abstract
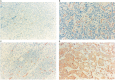
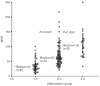
The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic influence of microvessel density using the hot spot method in 107 patients diagnosed with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. In each case, inflammation was found in the invasive carcinoma, therefore we classified the degree of inflammation as minimal, moderate or intense. Microvessel density was then reevaluated in each tumour in areas corresponding to these three categories. Median microvessel density irrespective of degree of inflammation was 71. Areas of minimal, moderate and intense inflammation were found in 48, 92 and 32 tumours. Microvessel density increased significantly with increasing degree of inflammation. Disease-specific survival was improved if areas of intense inflammation were present in the carcinoma (P=0.004). High microvessel density, irrespective of the degree of inflammation, was associated with a significantly better disease-specific survival (P=0.01). Multivariate analysis using death of disease as endpoint demonstrated an independent prognostic value of N-classification (N0, hazard ratio (HR)=1 vs N1, HR=2.89 (range, 1.52-5.52) vs N2, HR=3.61 (range, 1.84-7.08)), and intense inflammation, HR=0.48 (range, 0.24-0.96). Malignancy grade, T classification and microvessel density were not independent significant markers of poor outcome. In conclusion, inflammation was significantly correlated to microvessel density, and areas of intense inflammation were an independent marker of good prognosis.
Copyright 2002 Cancer Research UK
Figures



References
-
- AhlgrenJRisbergBVillmanKBerghJ2002Angiogenesis in invasive breast carcinoma–a prospective study of tumour heterogeneity Eur J Cancer 386469 - PubMed
-
- AlexandroffABJacksonAMO'DonnellMAJamesK1999BCG immunotherapy of bladder cancer: 20 years on Lancet 35316891694 - PubMed
-
- BassiPFerranteGDPiazzaNSpinadinRCarandoRPappagalloGPaganoF1999Prognostic factors of outcome after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a retrospective study of a homogeneous patient cohort J Urol 16114941497 - PubMed
-
- BergkvistALjungquistAMobergerG1965Classification of bladder tumours based on the cellular pattern. Preliminary report of a clinical-pathological study of 300 cases with a minimum follow-up of eight years Acta Chir Scand 130371378 - PubMed
-
- BlandJMAltmanDG1986Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement Lancet 1307310 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

