Nifedipine improves blood flow and oxygen supply, but not steady-state oxygenation of tumours in perfusion pressure-controlled isolated limb perfusion
- PMID: 12454778
- PMCID: PMC2376281
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600611
Nifedipine improves blood flow and oxygen supply, but not steady-state oxygenation of tumours in perfusion pressure-controlled isolated limb perfusion
Abstract
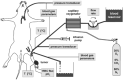
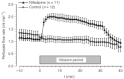
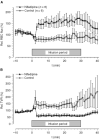
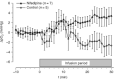
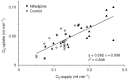
Isolated limb perfusion allows the direct application of therapeutic agents to a tumour-bearing extremity. The present study investigated whether the dihydropyridine-type Ca(2+)-channel blocker nifedipine could improve blood flow and oxygenation status of experimental tumours during isolated limb perfusion. Perfusion was performed by cannulation of the femoral artery and vein in rats bearing DS-sarcoma on the hind foot dorsum. Perfusion rate was adjusted to maintain a perfusion pressure of 100-140 mmHg throughout the experiment. Following equilibration, nifedipine was continuously infused for 30 min (8.3 microg min(-1) kg(-1) BW). During constant-pressure isolated limb perfusion, nifedipine can significantly increase perfusion rate (+100%) and RBC flux (+60%) through experimental leg tumours. "Steal phenomena" in favour of the surrounding normal tissue and oedema formation were not observed. Despite the increased oxygen availability (+63%) seen upon application of this calcium channel blocker, nifedipine does not result in a substantial reduction of tumour hypoxia, most probably due to an increase in O(2) uptake with rising O(2) supply to the tumour-bearing hind limb. Nifedipine application during isolated limb perfusion can enhance tumour microcirculation and may therefore promote the delivery (pharmacokinetics) of anti-cancer drugs to the tumour and by this improve the efficacy of pressure-controlled isolated limb perfusion.
Copyright 2002 Cancer Research UK
Figures
Similar articles
-
No improvement in perfusion and oxygenation of experimental tumors upon application of vasodilator drugs.Int J Oncol. 2001 Dec;19(6):1243-7. doi: 10.3892/ijo.19.6.1243. Int J Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11713595
-
Changes in microregional perfusion, oxygenation, ATP and lactate distribution in subcutaneous rat tumours upon water-filtered IR-A hyperthermia.Int J Hyperthermia. 1995 Mar-Apr;11(2):241-55. doi: 10.3109/02656739509022460. Int J Hyperthermia. 1995. PMID: 7790738
-
Disparate responses of tumour vessels to angiotensin II: tumour volume-dependent effects on perfusion and oxygenation.Br J Cancer. 2000 Jul;83(2):225-31. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1229. Br J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10901375 Free PMC article.
-
Localized hypothermia: impact on oxygenation, microregional perfusion, metabolic and bioenergetic status of subcutaneous rat tumours.Br J Cancer. 1998 Jul;78(1):56-61. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1998.442. Br J Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9662251 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of tumor oxygenation and red blood cell flux in response to inspiratory hyperoxia combined with different levels of inspiratory hypercapnia.Radiother Oncol. 2002 Jan;62(1):77-85. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(01)00401-7. Radiother Oncol. 2002. PMID: 11830315
Cited by
-
Anti-Cancer Agents in Proliferation and Cell Death: The Calcium Connection.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 20;20(12):3017. doi: 10.3390/ijms20123017. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31226817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BiaglowJEVarnesMEJacobsonBSuitHD1986Effect of calcium channel blocking drugs on tumor cell oxygen utilization Adv Exp Med Biol 200583589 - PubMed
-
- BonenAClarkMGHenriksenEJ1994Experimental approaches in muscle metabolism: hindlimb perfusion and isolated muscle incubations Am J Physiol 266E1E16 - PubMed
-
- CornwellMMPastanIGottesmanMM1987Certain calcium channel blockers bind specifically to multidrug-resistant human KB carcinoma membrane vesicles and inhibit drug binding to P-glycoprotein J Biol Chem 26221662170 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

