Statistical flattening of MEG beamformer images
- PMID: 12454907
- PMCID: PMC6871854
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.10072
Statistical flattening of MEG beamformer images
Abstract
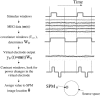
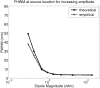
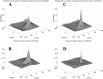
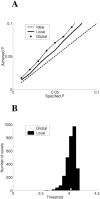
We propose a method of correction for multiple comparisons in MEG beamformer based Statistical Parametric Maps (SPMs). We introduce a modification to the minimum-variance beamformer, in which beamformer weights and SPMs of source-power change are computed in distinct steps. This approach allows the calculation of image smoothness based on the computed weights alone. In the first instance we estimate image smoothness by looking at local spatial correlations in residual images generated using random data; we then go on to show how the smoothness of the SPM can be obtained analytically by measuring the correlations between the adjacent weight vectors. In simulations we show that the smoothness of the SPM is highly inhomogeneous and depends on the source strength. We show that, for the minimum variance beamformer, knowledge of image smoothness is sufficient to allow for correction of the multiple comparison problem. Per-voxel threshold estimates, based on the voxels extent (or cluster size) in flattened space, provide accurate corrected false positive error rates for these highly inhomogeneously smooth images.
Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Barnes GR, Francis S, Hillebrand A, He J, Furlong PL, Bowtell RW, Singh KD, Holliday IE, Morris PG (2001): The spatial relationship between event‐related changes in cortical synchrony and the haemodynamic response. Neuroimage 13: S71.
-
- Capon J (1969): High‐resolution frequency‐wavenumber spectrum analysis. Proc IEEE 57: 1408–1419.
-
- Cheyne D, Barnes GR, Holliday IE, Furlong PL (2000): Localization of brain activity associated with non‐time‐locked tactile stimulation using synthetic aperture magnetometry (SAM) In: Neonen J, Ilmoniemi T, Katila T, editors. 12th International Conference on Biomagnetism. Espoo, Finland: Helsinki Univ. of Technology; p 255–258.
-
- Friston KJ, Holmes A, Poline JB, Price CJ, Frith CD (1996a): Detecting activations in PET and fMRI: levels of inference and power. Neuroimage 4: 223–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

