Pumilio homologue from saprolegnia parasitica specifically expressed in undifferentiated spore cysts
- PMID: 12455976
- PMCID: PMC118044
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.1.1.105-111.2002
Pumilio homologue from saprolegnia parasitica specifically expressed in undifferentiated spore cysts
Abstract
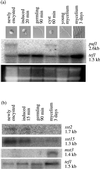
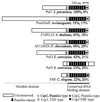
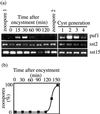
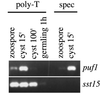
The expression of spore-specific marker transcripts at different stages of the asexual life cycle of Saprolegnia parasitica was analyzed. One of the markers, designated puf1, was found to be expressed transiently upon each of several cycles of zoospore encystment and reemergence. The transcript is induced immediately upon zoospore encystment and is rapidly lost when a cyst is triggered to germinate. In nongerminating cysts, puf1 is maintained until a time point when the cysts can no longer be triggered to germinate and thus have become determined for zoospore reemergence. The results show that the cyst stage has two phases, of about equal duration, which are physiologically and transcriptionally distinct and that the transcriptional machinery of oomycetes is also active in nongerminating spores. puf1 encodes a putative mRNA binding protein belonging to a conserved class of proteins including the Drosophila melanogaster Pumilio protein, Caenorhabditis elegans FBF, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Puf5, all of which are involved in regulation of gene expression by post-transcriptional mechanisms.
Figures



References
-
- Cerenius, L., and K. Söderhäll. 1984. Repeated zoospore emergence from isolated spore cysts of Aphanomyces astaci. Exp. Mycol. 8: 370–377.
-
- Cerenius, L., and K. Söderhäll. 1985. Repeated zoospore emergence as a possible adaptation to parasitism in Aphanomyces. Exp. Mycol. 9: 259–377.
-
- Cerenius, L., and K. Söderhäll. 1986. Saprolegniaceae: zoospore formation, virulence and pathogenesis in animal hosts, p. 97–116. In R. Dayal (ed.), Advances in zoosporic fungi. M D Publications Pvd. Ltd., New Delhi, India.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

