DNA methylation controls histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and heterochromatin assembly in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 12456661
- PMCID: PMC136960
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf657
DNA methylation controls histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and heterochromatin assembly in Arabidopsis
Abstract
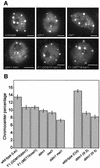
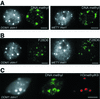
We propose a model for heterochromatin assembly that links DNA methylation with histone methylation and DNA replication. The hypomethylated Arabidopsis mutants ddm1 and met1 were used to investigate the relationship between DNA methylation and chromatin organization. Both mutants show a reduction of heterochromatin due to dispersion of pericentromeric low-copy sequences away from heterochromatic chromocenters. DDM1 and MET1 control heterochromatin assembly at chromocenters by their influence on DNA maintenance (CpG) methylation and subsequent methylation of histone H3 lysine 9. In addition, DDM1 is required for deacetylation of histone H4 lysine 16. Analysis of F(1) hybrids between wild-type and hypomethylated mutants revealed that DNA methylation is epigenetically inherited and represents the genomic imprint that is required to maintain pericentromeric heterochromatin.
Figures



References
-
- Bannister A.J., Zegerman,P., Partridge,J.F., Miska,E.A., Thomas,J.O., Allshire,R.C. and Kouzarides,T. (2001) Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature, 410, 120–124. - PubMed
-
- Belyaev N.D., Keohane,A.M. and Turner,B.M. (1996) Differential underacetylation of histones H2A, H3 and H4 on the inactive X chromosome in human female cells. Hum. Genet., 97, 573–578. - PubMed
-
- Casacuberta E., Casacuberta,J.M., Puigdomènech,P. and Monfort,A. (1998) Presence of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) in the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana: characterisation of the Emigrant family of elements. Plant J., 16, 79–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

