Elucidating TOR signaling and rapamycin action: lessons from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 12456783
- PMCID: PMC134654
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.66.4.579-591.2002
Elucidating TOR signaling and rapamycin action: lessons from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
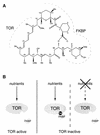
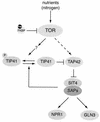
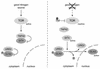
TOR (target of rapamycin) is a phosphatidylinositol kinase-related protein kinase that controls cell growth in response to nutrients. Rapamycin is an immunosuppressive and anticancer drug that acts by inhibiting TOR. The modes of action of TOR and rapamycin are remarkably conserved from S. cerevisiae to humans. The current understanding of TOR and rapamycin is derived largely from studies with S. cerevisiae. In this review, we discuss the contributions made by S. cerevisiae to understanding rapamycin action and TOR function.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

