Role of RAD52 epistasis group genes in homologous recombination and double-strand break repair
- PMID: 12456786
- PMCID: PMC134659
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.66.4.630-670.2002
Role of RAD52 epistasis group genes in homologous recombination and double-strand break repair
Abstract
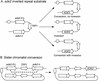
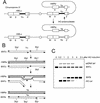
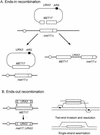
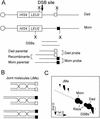
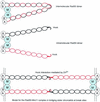
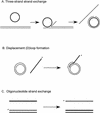
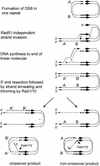
The process of homologous recombination is a major DNA repair pathway that operates on DNA double-strand breaks, and possibly other kinds of DNA lesions, to promote error-free repair. Central to the process of homologous recombination are the RAD52 group genes (RAD50, RAD51, RAD52, RAD54, RDH54/TID1, RAD55, RAD57, RAD59, MRE11, and XRS2), most of which were identified by their requirement for the repair of ionizing-radiation-induced DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The Rad52 group proteins are highly conserved among eukaryotes, and Rad51, Mre11, and Rad50 are also conserved in prokaryotes and archaea. Recent studies showing defects in homologous recombination and double-strand break repair in several human cancer-prone syndromes have emphasized the importance of this repair pathway in maintaining genome integrity. Although sensitivity to ionizing radiation is a universal feature of rad52 group mutants, the mutants show considerable heterogeneity in different assays for recombinational repair of double-strand breaks and spontaneous mitotic recombination. Herein, I provide an overview of recent biochemical and structural analyses of the Rad52 group proteins and discuss how this information can be incorporated into genetic studies of recombination.
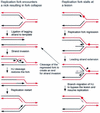
Figures







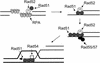
References
-
- Aguilera, A. 1995. Genetic evidence for different RAD52-dependent intrachromosomal recombination pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Genet. 27:298-305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

