Glucose-dependent regulation of rhythmic action potential firing in pancreatic beta-cells by K(ATP)-channel modulation
- PMID: 12456829
- PMCID: PMC2290696
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.031344
Glucose-dependent regulation of rhythmic action potential firing in pancreatic beta-cells by K(ATP)-channel modulation
Abstract
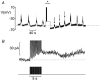
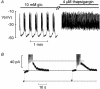
The regulation of a K(+) current activating during oscillatory electrical activity (I(K,slow)) in an insulin-releasing beta-cell was studied by applying the perforated patch whole-cell technique to intact mouse pancreatic islets. The resting whole-cell conductance in the presence of 10 mM glucose amounted to 1.3 nS, which rose by 50 % during a series of 26 simulated action potentials. Application of the K(ATP)-channel blocker tolbutamide produced uninterrupted action potential firing and reduced I(K,slow) by approximately 50 %. Increasing glucose from 15 to 30 mM, which likewise converted oscillatory electrical activity into continuous action potential firing, reduced I(K,slow) by approximately 30 % whilst not affecting the resting conductance. Action potential firing may culminate in opening of K(ATP) channels by activation of ATP-dependent Ca(2+) pumping as suggested by the observation that the sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA) inhibitor thapsigargin (4 microM) inhibited I(K,slow) by 25 % and abolished bursting electrical activity. We conclude that oscillatory glucose-induced electrical activity in the beta-cell involves the opening of K(ATP)-channel activity and that these channels, in addition to constituting the glucose-regulated K(+) conductance, also play a role in the graded response to supra-threshold glucose concentrations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of Ca(2+)-dependent K(+) channels contributes to rhythmic firing of action potentials in mouse pancreatic beta cells.J Gen Physiol. 1999 Dec;114(6):759-70. doi: 10.1085/jgp.114.6.759. J Gen Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10578013 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-gated and resting membrane currents recorded from B-cells in intact mouse pancreatic islets.J Physiol. 1999 Dec 15;521 Pt 3(Pt 3):717-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00717.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10601501 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Ca(2+) modulation of ATP-sensitive K(+) channel activity in acetylcholine-induced activation of rat pancreatic beta-cells.Endocrinology. 2002 Feb;143(2):569-76. doi: 10.1210/endo.143.2.8625. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 11796512
-
The beta-cell response to oral hypoglycemic agents.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995 Aug;28 Suppl:S81-9. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(95)01088-u. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995. PMID: 8529522 Review.
-
Electrophysiology of islet cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;654:115-63. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-3271-3_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20217497 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling K,ATP--dependent excitability in pancreatic islets.Biophys J. 2014 Nov 4;107(9):2016-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.09.037. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 25418087 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between membrane potential and cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in beta cells from Sur1-/- mice.Diabetologia. 2005 May;48(5):913-21. doi: 10.1007/s00125-005-1720-8. Epub 2005 Apr 14. Diabetologia. 2005. PMID: 15830184
-
Bursting and calcium oscillations in pancreatic beta-cells: specific pacemakers for specific mechanisms.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Oct;299(4):E517-32. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00177.2010. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20628025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The triggering pathway to insulin secretion: Functional similarities and differences between the human and the mouse β cells and their translational relevance.Islets. 2017 Nov 2;9(6):109-139. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2017.1342022. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Islets. 2017. PMID: 28662366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An adenylate kinase is involved in KATP channel regulation of mouse pancreatic beta cells.Diabetologia. 2007 Oct;50(10):2126-34. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0742-9. Epub 2007 Aug 18. Diabetologia. 2007. PMID: 17704905
References
-
- Ämmälä C, Larsson O, Berggren PO, Bokvist K, Juntti-berggren L, Kindmark H, Rorsman P. Inositol trisphosphate-dependent activation of a Ca2+-activated K+-conductance in glucose-stimulated pancreatic β -cells. Nature. 1991;353:849–852. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. 1989;54:87–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

