Excitability of human muscle afferents studied using threshold tracking of the H reflex
- PMID: 12456841
- PMCID: PMC2290676
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.026526
Excitability of human muscle afferents studied using threshold tracking of the H reflex
Abstract
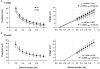
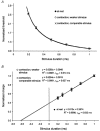
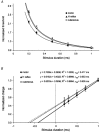
In human peripheral nerves, physiological evidence has been presented for a number of biophysical differences between cutaneous afferents and alpha motor axons. The differences in strength-duration properties for cutaneous afferents and motor axons in the median nerve have been attributed to greater expression of a persistent Na(+) conductance (I(Na,P)) on cutaneous afferents. However, it is unclear whether the biophysical properties of human group Ia afferents differ from those of cutaneous afferents. The present studies were undertaken to determine whether the properties of human group Ia afferents can be studied indirectly using 'threshold tracking' to measure the excitability changes in the H reflex, and to determine whether the excitability of group Ia afferents differs from that of cutaneous afferents. The strength-duration properties of the soleus H reflex and soleus motor axons were measured at rest and during sustained voluntary contractions. Similar experiments were performed on the median nerve at the wrist to study the strength-duration properties of cutaneous afferents, alpha motor axons and H reflex of the thenar muscles. In addition, the technique of 'latent addition' was used to determine whether there was a difference in a low-threshold conductance on soleus Ia afferent and motor axons. The present findings indicate that the strength-duration time constant (tau(SD)) for the H reflex is longer than that for alpha motor axons, but similar to that for cutaneous afferents. There were no differences in tau(SD) for the soleus H reflex at rest and during contractions, suggesting that tau(SD) for the H reflex is largely unaffected by changes in synaptic or motoneurone properties. Finally, the difference in latent addition suggests that the longer tau(SD) of the soleus H reflex may indeed be due to greater activity of a persistent Na(+) conductance on Ia afferents than on soleus alpha motor axons.
Figures
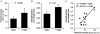
References
-
- Baker MD, Bostock H. Low-threshold, persistent sodium current in rat large dorsal root ganglion neurons in culture. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1997;77:1503–1513. - PubMed
-
- Bostock H, Baker M. Evidence for two types of potassium channel in human motor axons in vivo. Brain Research. 1988;462:354–358. - PubMed
-
- Bostock H, Burke D, Hales JP. Differences in behaviour of sensory and motor axons following release of ischaemia. Brain. 1994;117:225–234. - PubMed
-
- Bostock H, Cikurel K, Burke D. Threshold tracking techniques in the study of human peripheral nerve. Muscle and Nerve. 1998;21:137–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

