Murine apolipoprotein serum amyloid A in solution forms a hexamer containing a central channel
- PMID: 12456883
- PMCID: PMC138545
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.252508399
Murine apolipoprotein serum amyloid A in solution forms a hexamer containing a central channel
Abstract
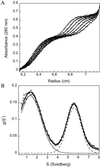
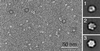
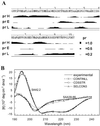
Serum amyloid A (SAA) is a small apolipoprotein that binds to high-density lipoproteins in the serum. Although SAA seems to play a role in host defense and lipid transport and metabolism, its specific functions have not been defined. Despite the growing implications that SAA plays a role in the pathology of various diseases, a high-resolution structure of SAA is lacking because of limited solubility in the high-density lipoprotein-free form. In this study, complementary methods including glutaraldehyde cross-linking, size-exclusion chromatography, and sedimentation-velocity analytical ultracentrifugation were used to show that murine SAA2.2 in aqueous solution exists in a monomer-hexamer equilibrium. Electron microscopy of hexameric SAA2.2 revealed that the subunits are arranged in a ring forming a putative central channel. Limited trypsin proteolysis and mass spectrometry analysis identified a significantly protease-resistant SAA2.2 region comprising residues 39-86. The isolated 39-86 SAA2.2 fragment did not hexamerize, suggesting that part of the N terminus is involved in SAA2.2 hexamer formation. Circular-dichroism spectrum deconvolution and secondary-structure prediction suggest that SAA2.2 contains approximately 50% of its residues in alpha-helical conformation and <10% in beta-structure. These findings are consistent with the recent discovery that human SAA1.1 forms a membrane channel and have important implications for understanding the 3D structure, multiple functions, and pathological roles of this highly conserved protein.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Urea-induced denaturation of apolipoprotein serum amyloid A reveals marginal stability of hexamer.Protein Sci. 2005 Jul;14(7):1811-7. doi: 10.1110/ps.051387005. Epub 2005 Jun 3. Protein Sci. 2005. PMID: 15937280 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between apolipoprotein serum amyloid A and high-density lipoprotein.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Apr 23;317(1):157-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.03.027. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15047161
-
From hexamer to amyloid: marginal stability of apolipoprotein SAA2.2 leads to in vitro fibril formation at physiological temperature.Amyloid. 2005 Sep;12(3):139-48. doi: 10.1080/13506120500223084. Amyloid. 2005. PMID: 16194868
-
Effect of zinc, copper, and calcium on the structure and stability of serum amyloid A.Biochemistry. 2007 May 8;46(18):5562-9. doi: 10.1021/bi602629y. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17425332
-
Intrinsic Stability, Oligomerization, and Amyloidogenicity of HDL-Free Serum Amyloid A.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;855:117-34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-17344-3_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26149928 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum amyloid A 2.2 refolds into a octameric oligomer that slowly converts to a more stable hexamer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Apr 22;407(4):725-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.090. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21439938 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble pattern recognition molecules: Guardians and regulators of homeostasis at airway mucosal surfaces.Eur J Immunol. 2020 May;50(5):624-642. doi: 10.1002/eji.201847811. Eur J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32246830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The turning away of serum amyloid A biological activities and receptor usage.Immunology. 2021 Jun;163(2):115-127. doi: 10.1111/imm.13295. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33315264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum amyloid A - a review.Mol Med. 2018 Aug 30;24(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0047-0. Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30165816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid peptide channels.J Membr Biol. 2004 Nov;202(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00232-004-0709-4. J Membr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15702375 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

