Pushing the limits of the scanning mechanism for initiation of translation
- PMID: 12459250
- PMCID: PMC7126118
- DOI: 10.1016/s0378-1119(02)01056-9
Pushing the limits of the scanning mechanism for initiation of translation
Abstract
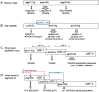
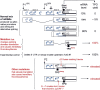
Selection of the translational initiation site in most eukaryotic mRNAs appears to occur via a scanning mechanism which predicts that proximity to the 5' end plays a dominant role in identifying the start codon. This "position effect" is seen in cases where a mutation creates an AUG codon upstream from the normal start site and translation shifts to the upstream site. The position effect is evident also in cases where a silent internal AUG codon is activated upon being relocated closer to the 5' end. Two mechanisms for escaping the first-AUG rule--reinitiation and context-dependent leaky scanning--enable downstream AUG codons to be accessed in some mRNAs. Although these mechanisms are not new, many new examples of their use have emerged. Via these escape pathways, the scanning mechanism operates even in extreme cases, such as a plant virus mRNA in which translation initiates from three start sites over a distance of 900 nt. This depends on careful structural arrangements, however, which are rarely present in cellular mRNAs. Understanding the rules for initiation of translation enables understanding of human diseases in which the expression of a critical gene is reduced by mutations that add upstream AUG codons or change the context around the AUG(START) codon. The opposite problem occurs in the case of hereditary thrombocythemia: translational efficiency is increased by mutations that remove or restructure a small upstream open reading frame in thrombopoietin mRNA, and the resulting overproduction of the cytokine causes the disease. This and other examples support the idea that 5' leader sequences are sometimes structured deliberately in a way that constrains scanning in order to prevent harmful overproduction of potent regulatory proteins. The accumulated evidence reveals how the scanning mechanism dictates the pattern of transcription--forcing production of monocistronic mRNAs--and the pattern of translation of eukaryotic cellular and viral genes.
Figures


References
-
- Aarnoudse C.A., van den Doel P.B., Heemskerk B., Schrier P.I. Interleukin-2-induced, melanoma-specific T cells recognize CAMEL, an unexpected translation product of LAGE-1. Int. J. Cancer. 1999;82:442–448. - PubMed
-
- Acland P., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Subcellular fate of the Int-2 oncoprotein is determined by choice of initiation codon. Nature. 1990;343:662–665. - PubMed
-
- Afshar-Kharghan V., Li C.Q., Khoshnevis-Asi M., López J.A. Kozak sequence polymorphism of the glycoprotein (GP) Ibα gene is a major determinant of the plasma membrane levels of the platelet GP Ib-IX-V complex. Blood. 1999;94:186–191. - PubMed
-
- Aho S., Levänsuo L., Montonen O., Kari C., Rodeck U., Uitto J. Specific sequences in p120ctn determine subcellular distribution of its multiple isoforms involved in cellular adhesion of normal and malignant epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:1391–1402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

