Expression and regulation of ST2, an interleukin-1 receptor family member, in cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction
- PMID: 12460879
- PMCID: PMC1460012
- DOI: 10.1161/01.cir.0000038705.69871.d9
Expression and regulation of ST2, an interleukin-1 receptor family member, in cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: We identified an interleukin-1 receptor family member, ST2, as a gene markedly induced by mechanical strain in cardiac myocytes and hypothesized that ST2 participates in the acute myocardial response to stress and injury.
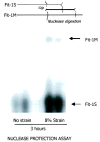
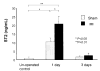
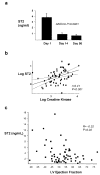
Methods and results: ST2 mRNA was induced in cardiac myocytes by mechanical strain (4.7+/-0.9-fold) and interleukin-1beta (2.0+/-0.2-fold). Promoter analysis revealed that the proximal and not the distal promoter of ST2 is responsible for transcriptional activation in cardiac myocytes by strain and interleukin-1beta. In mice subjected to coronary artery ligation, serum ST2 was transiently increased compared with unoperated controls (20.8+/-4.4 versus 0.8+/-0.8 ng/mL, P<0.05). Soluble ST2 levels were increased in the serum of human patients (N=69) 1 day after myocardial infarction and correlated positively with creatine kinase (r=0.41, P<0.001) and negatively with ejection fraction (P=0.02).
Conclusions: These data identify ST2 release in response to myocardial infarction and suggest a role for this innate immune receptor in myocardial injury.
Figures


References
-
- Iwahana H, Yanagisawa K, Ito-Kosaka A, et al. Different promoter usage and multiple transcription initiation sites of the interleukin-1 receptor-related human ST2 gene in UT-7 and TM12 cells. Eur J Biochem. 1999;264:397–406. - PubMed
-
- Tominaga S. A putative protein of a growth specific cDNA from BALB/c-3T3 cells is highly similar to the extracellular portion of mouse interleukin-1 receptor. FEBS Lett. 1989;258:301–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

