Essential role for the C5a receptor in regulating the effector phase of synovial infiltration and joint destruction in experimental arthritis
- PMID: 12461081
- PMCID: PMC2194257
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20020205
Essential role for the C5a receptor in regulating the effector phase of synovial infiltration and joint destruction in experimental arthritis
Abstract
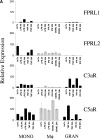
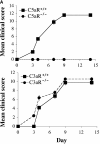
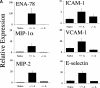
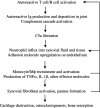
A characteristic feature of rheumatoid arthritis is the abundance of inflammatory cells in the diseased joint. Two major components of this infiltrate are neutrophils in the synovial fluid and macrophages in the synovial tissue. These cells produce cytokines including tumor necrosis factor alpha and other proinflammatory mediators that likely drive the disease through its effector phases. To investigate what mechanisms underlie the recruitment of these cells into the synovial fluid and tissue, we performed expression analyses of chemoattractant receptors in a related family that includes the anaphylatoxin receptors and the formyl-MetLeuPhe receptor. We then examined the effect of targeted disruption of two abundantly expressed chemoattractant receptors, the receptors for C3a and C5a, on arthritogenesis in a mouse model of disease. We report that genetic ablation of C5a receptor expression completely protects mice from arthritis.
Figures







References
-
- Firestein, G.S. 1996. Invasive fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum. 39:1781–1790. - PubMed
-
- Choy, E.H., and G.S. Panayi. 2001. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 344:907–916. - PubMed
-
- Fox, D.A. 1997. The role of T cells in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: new perspectives. Arthritis Rheum. 40:598–609. - PubMed
-
- Plater-Zyberk, C., A.J. Hoogewerf, A.E. Proudfoot, C.A. Power, and T.N. Wells. 1997. Effect of a CC chemokine receptor antagonist on collagen induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. Immunol. Lett. 57:117–120. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

