Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of estrogen receptor-alpha by TGF-beta1 in breast cancer cell lines
- PMID: 12461787
- PMCID: PMC2572568
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.10353
Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of estrogen receptor-alpha by TGF-beta1 in breast cancer cell lines
Abstract
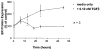
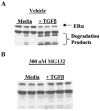
Normal mammary epithelial cells are rapidly induced to G(1) arrest by the widely expressed cytokine, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta1). Studies in established breast cancer cell lines that express the estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) have demonstrated loss of this responsiveness. This inverse correlation suggests interpathway signaling important to cell growth and regulation. The adenocarcinoma breast cell line BT474, which was not growth arrested by TGF-beta1, was used as a model of estrogen-inducible growth to explore interpathway crosstalk. Although BT474 cells were not growth-arrested by TGF-beta1 as determined by flow cytometry analysis and 5'-bromo-3'-deoxyuridine incorporation into DNA, estrogen receptor protein levels were attenuated by 100 pM TGF-beta1 after 6 h. This decrease in ERalpha reached 50% of untreated control levels by 24 h of treatment and was further supported by a 50% decrease in estrogen-inducible DNA synthesis. Inspection of ERalpha transcripts suggested that this decrease was primarily the result of altered ERalpha protein stability or availability. Use of the proteasome inhibitor, MG132, abolished all effects on ERalpha by TGF-beta1. Collectively, this data supports a role for TGF-beta1 in regulating the growth of otherwise insensitive breast cancer cells through modulation of ERalpha stability.
Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
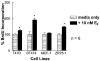
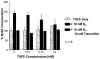
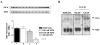
References
-
-
American Cancer Society. 2001. Facts and figures.
-
-
- Arteaga CL, Tandon AK, Von Hoff DD, Osborne CK. Transforming growth factor beta: Potential autocrine growth inhibitor of estrogen receptor-negative human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1988;48:3898–3904. - PubMed
-
- Baudino TA, Kraichely DM, Jefcoat SC, Jr, Winchester SK, Partridge NC, MacDonald PN. Isolation and characterization of a novel coactivator protein, NCoA-62, involved in vitamin D-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:16434–16441. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein L, Henderson BE, Hanisch R, Sullivan-Halley J, Ross RK. Physical exercise and reduced risk of breast cancer in young women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994;86:1403–1408. - PubMed
-
- Bonni S, Wang HR, Causing CG, Kavsak P, Stroschein SL, Luo K, Wrana JL. TGF-beta induces assembly of a Smad2–Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase complex that targets SnoN for degradation. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:587–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

