Neutrophils and lung injury: getting it right
- PMID: 12464663
- PMCID: PMC151642
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI17302
Neutrophils and lung injury: getting it right
Figures
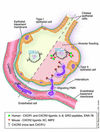
Comment on
-
Critical role for CXCR2 and CXCR2 ligands during the pathogenesis of ventilator-induced lung injury.J Clin Invest. 2002 Dec;110(11):1703-16. doi: 10.1172/JCI15849. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12464676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NIH ARDSNet Group. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1301–1308. - PubMed
-
- Dreyfuss D, Saumon G. Ventilator-induced lung injury: lessons from experimental studies. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:294–323. - PubMed
-
- Dos Santos CC, Slutsky AS. Mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury: a perspective. J Appl Physiol. 2000;89:1645–1655. - PubMed
-
- Ranieri VM, et al. Effect of mechanical ventilation on inflammatory mediators in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999;282:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Repine JE, Beehler CJ. Neutrophils and the adult respiratory distress syndrome: two interlocking perspectives. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;144:251–252. - PubMed

