Differential expression of LIGHT and its receptors in human placental villi and amniochorion membranes
- PMID: 12466117
- PMCID: PMC1850908
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64479-3
Differential expression of LIGHT and its receptors in human placental villi and amniochorion membranes
Abstract
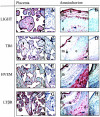
mRNA encoding LIGHT (homologous to lymphotoxins, exhibits inducible expression, competes with herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D for HVEM, a receptor expressed by T lymphocytes), a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily of ligands, as well as mRNAs encoding LIGHT receptors [HVEM, LTbetaR, and TR6 (DcR3)] are present in placentas and cytotrophoblast cells at term. To establish translation of these messages and determine directions for functional studies, term placentas, amniochorion membranes, and purified cytotrophoblast cells were evaluated by immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry. Ligand and receptor proteins were identified in lysates from all three sources although the soluble receptor, TR6, was scarce in placentas and all receptors were in low abundance in cytotrophoblast cells. These results were confirmed and cell type-specific expression was documented by immunohistochemistry. Ligand and receptor proteins were differentially expressed according to cell type. For example, HVEM was identified on syncytiotrophoblast but not in villous mesenchymal cells; amnion epithelial cells were positive for all proteins whereas chorion membrane cytotrophoblasts exhibited none. Because LIGHT is a powerful cytokine that can alter gene expression and promote apoptosis, these experiments suggest that ligand-receptor interactions may critically influence structural and functional aspects of human placentas through as yet undefined autocrine/paracrine pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Phillips TA, Ni J, Pan G, Ruben SM, Wei Y, Pace J, Hunt JS: TRAIL (Apo-2L) and TRAIL receptors in human placentas: implications for immune privilege. J Immunol 1999, 162:6053-6059 - PubMed
-
- Runic R, Lockwood CJ, Ma Y, Dipasquale B, Guller S: Expression of Fas ligand by human cytotrophoblasts: implications in placentation and fetal survival. J Clin Endocrinol 1996, 81:3119-3122 - PubMed
-
- Hunt JS, Vassmer D, Ferguson TA, Miller L: Fas ligand is positioned in mouse uterus and placenta to prevent trafficking of activated leukocytes between the mother and the conceptus. J Immunol 1997, 158:4122-4128 - PubMed
-
- Phillips TA, Ni J, Hunt JS: Death-inducing tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily ligands and receptors are transcribed in human placentas, cytotrophoblasts, placental macrophages, and placental cell lines. Placenta 2001, 22:663-672 - PubMed
-
- Mauri DN, Ebner R, Montgomery RI, Kochel KD, Cheung TC, Yu GL, Ruben S, Murphy M, Eisenberg RJ, Cohen GH, Spear P, Ware C: LIGHT, a new member of the TNF superfamily, and lymphotoxic α are ligands for herpesvirus entry mediator. Immunity 1998, 8:21-30 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

