CD44 deficiency leads to enhanced neutrophil migration and lung injury in Escherichia coli pneumonia in mice
- PMID: 12466136
- PMCID: PMC1850923
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64498-7
CD44 deficiency leads to enhanced neutrophil migration and lung injury in Escherichia coli pneumonia in mice
Abstract
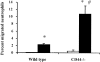
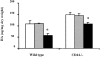
CD44 is a major cell-surface receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA), a glycosaminoglycan component of extracellular matrix. HA-CD44 interactions have been implicated in leukocyte extravasation into an inflammatory site. This study examined the role of CD44 in acute inflammatory responses during pneumonias induced by Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pneumoniae using CD44-deficient mice. In E. coli-induced pneumonia, neutrophil accumulation in the lungs and edema formation was increased by 84% and 88%, respectively, in CD44-deficient mice compared to wild-type mice. In contrast, no difference was observed between these genotypes in S. pneumoniae-induced pneumonia, and the HA content in the lungs decreased after instillation of S. pneumoniae, but not E. coli, in both genotypes. Studies to determine the mechanisms for this enhanced response showed that: 1) neutrophil apoptosis was not different between these two genotypes in either type of pneumonia; 2) CD44 deficiency resulted in enhanced mRNA expression of several inflammatory genes; and 3) CD44-deficient neutrophils migrated through Matrigel in response to chemoattractants faster and in greater numbers than wild-type neutrophils in vitro and this increase was in part dependent on HA content in the Matrigel. These data demonstrate that CD44 deficiency results in enhanced inflammation in E. coli but not S. pneumoniae-induced pneumonia, suggesting a previously unrecognized role for CD44 in limiting the inflammatory response to E. coli.
Figures

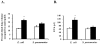

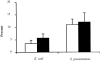

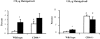

References
-
- Behzad AR, Chu F, Walker DC: Fibroblasts are in a position to provide directional information to migrating neutrophils during pneumonia in rabbit lungs. Microvasc Res 1996, 51:303-316 - PubMed
-
- Hogg JC, Doerschuk CM: Leukocyte traffic in the lung. Annu Rev Physiol 1995, 57:97-114 - PubMed
-
- Gebb SA, Graham JA, Hanger CC, Godbey PS, Capen RL, Doerschuk CM, Wagner WW: Sites of leukocyte sequestration in the pulmonary microcirculation. J Appl Physiol 1995, 79:493-497 - PubMed
-
- Doerschuk CM, Winn RK, Coxson HO, Harlan JM: CD18-dependent and -independent mechanisms of neutrophil emigration in the pulmonary and systemic microcirculation of rabbits. J Immunol 1990, 144:2327-2333 - PubMed
-
- Walker DC, Behzad AR, Chu F: Neutrophil migration through preexisting holes in the basal laminae of alveolar capillaries and epithelium during streptococcal pneumonia. Microvasc Res 1995, 50:397-416 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

