Inhibitory mechanism of xestospongin-C on contraction and ion channels in the intestinal smooth muscle
- PMID: 12466229
- PMCID: PMC1573613
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704988
Inhibitory mechanism of xestospongin-C on contraction and ion channels in the intestinal smooth muscle
Abstract
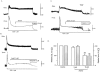
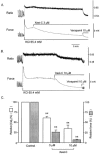
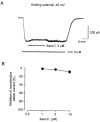
1. Xestospongin-C isolated from a marine sponge, Xestospongia sp., has recently been shown to be a membrane-permeable IP(3) receptor inhibitor. In this study we examined the effects of this compound on smooth muscle from guinea-pig ileum. 2. In guinea-pig ileum permeabilized with alpha-toxin, xestospongin-C (3 microM) inhibited contractions induced by Ca(2+) mobilized from sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) with IP(3) or carbachol with GTP, but not with caffeine. 3. In intact smooth muscle tissue, xestospongin-C (3-10 microM) inhibited carbachol- and high-K+-induced increases in [Ca(2+)](i) and contractions at sustained phase. 4. It also inhibited voltage-dependent inward Ba(2+) currents in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC(50) of 0.63 microM. Xestospongin-C (3-10 microM) had no effect on carbachol-induced inward Ca(2+) currents via non-selective cation channels; but it did reduce voltage-dependent K+ currents in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC(50) of 0.13 microM. 5. These results suggest that xestospongin-C inhibits the IP(3) receptor but not the ryanodine receptor in smooth muscle SR membrane. In intact smooth muscle cells, however, xestospongin-C appears to inhibit voltage-dependent Ca(2+) and K+ currents at a concentration range similar to that at which it inhibits the IP(3) receptor. Xestospongin-C is a selective blocker of the IP(3) receptor in permeabilised cells but not in cells with intact plasma membrane.
Figures



References
-
- DE SMET P., PARYS J.B., CALLEWAERT G., WEIDEMA A.F., HILL E., DE SMEDT H., ERNEUX C., SORRENTINO V., MISSIAEN L. Xestospongin-C is an equally potent inhibitor of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor and the endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+ pumps. Cell Calcium. 1999;26:9–13. - PubMed
-
- FABIATO A. Myoplasmic free calcium concentration reached during the twitch of an intact isolated cardiac cell and during calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned cardiac cell from the adult rat or rabbit ventricle. J. Gen. Physiol. 1981;78:457–497. - PMC - PubMed
-
- GAFNI J., MUNSCH J.A., LAM T.H., CATLIN M.C., COSTA L.G., MOLINSKI T.F., PESSAH L.N. Xestospongins: Potent membrane permeable blockers of the inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor. Neuron. 1997;19:723–733. - PubMed
-
- HU Q., DESHPANDE S., IRANI K., ZIEGELSTEIN R.C. [Ca2+]i oscillation frequency regulates agonist-stimulated NF-κB transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:33995–33998. - PubMed
-
- HOLDEN C.P., HAUGHEY N.J., DOLHUN B., SHEPEL P.N., NATH A., GEIGER J.D. Diadenosine pentaphosphate increases levels of intracellular calcium in astrocytes by a mechanism involving release from caffeine/ryanodine- and IP3-sensitive stores. J. Neuroscience Res. 2000;59:276–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

