Hormonal-dependent recruitment of Na+,K+-ATPase to the plasmalemma is mediated by PKC beta and modulated by [Na+]i
- PMID: 12466249
- PMCID: PMC1573600
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704962
Hormonal-dependent recruitment of Na+,K+-ATPase to the plasmalemma is mediated by PKC beta and modulated by [Na+]i
Abstract
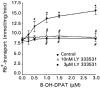
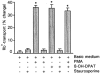
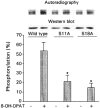
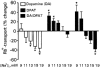
1. The present study demonstrates that stimulation of hormonal receptors of proximal tubule cells with the serotonin-agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetraline (8-OH-DPAT) induces an augmentation of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity that results from the recruitment of enzyme molecules to the plasmalemma. 2. Cells expressing the rodent wild-type Na(+),K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit had the same basal Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity as cells expressing the alpha-subunit S11A or S18A mutants, but stimulation of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity was completely abolished in either mutant. 3. 8-OH-DPAT treatment of OK cells led to PKC(beta)-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha-subunit Ser-11 and Ser-18 residues, and determination of enzyme activity with the S11A and S18A mutants indicated that both residues are essential for the agonist-dependent stimulation of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity. 4. When cells were treated with both dopamine and 8-OH-DPAT, an activation of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase was observed at basal intracellular sodium concentration (approximately 9 mM), and this activation was gradually reduced and became a significant inhibition as the concentration of intracellular sodium gradually increased from 9 to 19 mM. Thus, besides the antagonistic effects of dopamine and 8-OH-DPAT, intracellular sodium modulates whether an activation or an inhibition of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase is produced.
Figures


References
-
- APERIA A.C. Intrarenal dopamine: a key signal in the interactive regulation of sodium metabolism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000;62:621–647. - PubMed
-
- ASANO S., MATSUDA S., HOSHINA S., SAKAMOTO S., TAKEGUCHI N. A chimeric gastric H+,K+-ATPase inhibitable with both ouabain and SCH 28080. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:6848–6854. - PubMed
-
- BERTORELLO A.M., KATZ A.I. Short-term regulation of renal Na-K-ATPase activity: physiological relevance and cellular mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. 1993;265:F743–F755. - PubMed
-
- BERTORELLO A.M., RIDGE K.M., CHIBALIN A.V., KATZ A.I., SZNAJDER J. Isoproterenol increases Na+-K+-ATPase activity by membrane insertion of alpha-subunits in lung alveolar cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;276:L20–L27. - PubMed
-
- CHIBALIN A.V., OGIMOTO G., PEDEMONTE C.H., PRESSLEY T.A., KATZ A.I., FÉRAILLE E., BERGGREN P.-O., BERTORELLO A.M. Dopamine-induced endocytosis of Na+,K+-ATPase is initiated by phosphorylation of Ser-18 in the rat alpha subunit and is responsible for the decreased activity in epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:1920–1927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

