The mitogenic potential of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor in the human endometrium is mediated by the epidermal growth factor receptor and is modulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- PMID: 12466384
- PMCID: PMC1635788
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2002-020069
The mitogenic potential of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor in the human endometrium is mediated by the epidermal growth factor receptor and is modulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha
Abstract
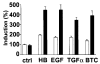
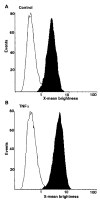
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF), a member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, is implicated in a variety of biological processes, including reproduction. Previous studies describe increased levels of HB-EGF in the human endometrium during the midsecretory stage of the menstrual cycle, suggesting a function for HB-EGF in implantation of the human blastocyst. Here we have investigated the expression and function of the soluble and transmembrane forms of HB-EGF in the human endometrium. We show that the expression of the transmembrane form of HB-EGF in the human endometrium is modulated according to the stage of the menstrual cycle. We present data demonstrating that both the soluble and transmembrane forms of HB-EGF induce DNA synthesis in human endometrial stromal cells. Furthermore, TNFalpha has a cooperative effect on HB-EGF, EGF, TGFalpha, and betacellulin-induced DNA synthesis in stromal cells, suggesting roles for the EGF family and TNFalpha in regeneration and maturation of human endometrium. Induction of DNA synthesis by HB-EGF and its modulation by TNFalpha in endometrial stromal cells are mediated by the EGF receptor and not the HB-EGF receptor ErbB4. Our data suggest key functions for HB-EGF, TNFalpha, and the EGF receptor in endometrial maturation, via autocrine/paracrine and juxtacrine pathways, in preparation for embryo implantation.
Figures




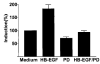
References
-
- Higashiyama S, Abraham JA, Miller J, Fiddes JC, Klagsbrun M. A heparin-binding growth factor secreted by macrophage-like cells that is related to EGF. Science. 1991;251:936–939. - PubMed
-
- Raab G, Klagsbrun M. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1333:F179–199. - PubMed
-
- Arkonac BM, Foster LC, Sibinga NE, Patterson C, Lai K, Tsai JC, Lee ME, Perrella MA, Haber E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in vascular endothelial cells [published erratum appears in J Biol Chem 1998 Apr 10;273(15):9352] J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4400–4405. - PubMed
-
- Abraham JA, Damm D, Bajardi A, Miller J, Klagsbrun M, Ezekowitz RA. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor: characterization of rat and mouse cDNA clones, protein domain conservation across species, and transcript expression in tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;190:125–133. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy TG, Brown KD, Vaughan TJ. Expression of the genes for the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in porcine oviduct and endometrium. Biol Reprod. 1994;50:751–756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

