Elucidation of structure-function relationships in the protein subunit of bacterial RNase P using a genetic complementation approach
- PMID: 12466529
- PMCID: PMC137979
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkf670
Elucidation of structure-function relationships in the protein subunit of bacterial RNase P using a genetic complementation approach
Abstract
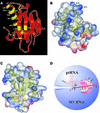
RNase P is a ribonucleoprotein involved in tRNA biosynthesis in all living organisms. Bacterial RNase P is comprised of a catalytic RNA subunit and a lone protein cofactor which plays a supporting, albeit essential, role in the tRNA processing reaction in vivo. In this study, we have searched various databases to identify homologs of the protein subunit of RNase P from diverse bacteria and used an alignment of their primary sequences to determine the most highly conserved residues, and thereby extend earlier predictions of which residues might play an important role in RNA recognition. By employing a genetic complementation assay, we have also gained insights into structure- function relationships in the protein subunit of bacterial RNase P.
Figures




References
-
- Altman S. and Kirsebom,L.A. (1999) Ribonuclease P. In Gesteland,R.F., Cech,T. and Atkins,J.F. (eds), The RNA World, 2nd Edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 351–380.
-
- Harris M.E., Frank,D. and Pace,N.R. (1998) Structure and catalytic function of the bacterial ribonuclease P ribozyme. In Simons,R.W. and Grunberg-Manago,M. (eds), RNA structure and function. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 309–337.
-
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner,K., Marsh,T., Pace,N.R. and Altman,S. (1983) The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell, 35, 849–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

