Adenosine: a neuron-glial transmitter promoting myelination in the CNS in response to action potentials
- PMID: 12467589
- PMCID: PMC1201407
- DOI: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)01067-x
Adenosine: a neuron-glial transmitter promoting myelination in the CNS in response to action potentials
Abstract
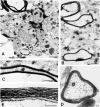
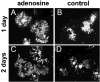
Neuronal activity influences myelination of the brain, but the molecular mechanisms involved are largely unknown. Here, we report that oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) express functional adenosine receptors, which are activated in response to action potential firing. Adenosine acts as a potent neuron-glial transmitter to inhibit OPC proliferation, stimulate differentiation, and promote the formation of myelin. This neuron-glial signal provides a molecular mechanism for promoting oligodendrocyte development and myelination in response to impulse activity and may help resolve controversy on the opposite effects of impulse activity on myelination in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Figures
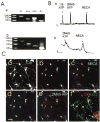
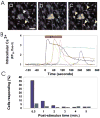
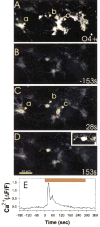
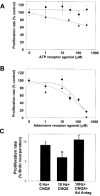
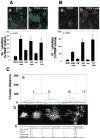
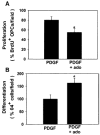
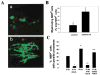
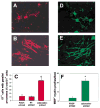
References
-
- Barres BA, Raff MC. Proliferation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells depends on electrical activity in axons. Nature. 1993;361:258–260. - PubMed
-
- Barres BA, Lazar MA, Raff MC. A novel role for thyroid hormone, glucocorticoids and retinoic acid in timing oligodendrocyte development. Development. 1994;120:1097–1108. - PubMed
-
- Baumann N, Pham-Dinh D. Biology of oligodendrocyte and myelin in the mammalian central nervous system. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:871–927. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

