An Ethiopian pattern of human adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia
- PMID: 12471159
- PMCID: PMC139295
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.252649199
An Ethiopian pattern of human adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia
Abstract
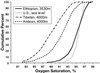
We describe, in Ethiopia, a third successful pattern of human adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia that contrasts with both the Andean "classic" (erythrocytosis with arterial hypoxemia) and the more recently identified Tibetan (normal venous hemoglobin concentration with arterial hypoxemia) patterns. A field survey of 236 Ethiopian native residents at 3,530 m (11,650 feet), 14-86 years of age, without evidence of iron deficiency, hemoglobinopathy, or chronic inflammation, found an average hemoglobin concentration of 15.9 and 15.0 gdl for males and females, respectively, and an average oxygen saturation of hemoglobin of 95.3%. Thus, Ethiopian highlanders maintain venous hemoglobin concentrations and arterial oxygen saturation within the ranges of sea level populations, despite the unavoidable, universal decrease in the ambient oxygen tension at high altitude.
Figures


References
-
- Winslow R. M. & Monge, C., (1987) Hypoxia, Polycythemia, and Chronic Mountain Sickness (Johns Hopkins Univ. Press, Baltimore).
-
- Beall C. M. (2000) in Oxygen Sensing: Molecule to Man, ed. Forster, R. E., II (Kluwer Academic, New York), pp. 63–74.
-
- Severinghaus J. W. & Naifeh, K. H. (1987) Anesthesiology 67, 551-558. - PubMed
-
- Nickerson B. G., Sarkisian, C. & Tremper, K. (1988) Chest 93, 515-517. - PubMed
-
- Adler J. N., Hugher, L. A., Vivilecchia, R. & Camargo, C. A. (1998) Acad. Emer. Med. 5, 965-970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

