Microtubule release from the centrosome in migrating cells
- PMID: 12473683
- PMCID: PMC2173398
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200207076
Microtubule release from the centrosome in migrating cells
Abstract
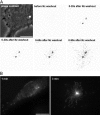
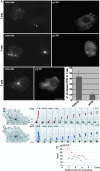
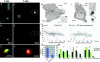
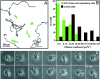
In migrating cells, force production relies essentially on a polarized actomyosin system, whereas the spatial regulation of actomyosin contraction and substrate contact turnover involves a complex cooperation between the microtubule (MT) and the actin filament networks (Goode, B.L., D.G. Drubin, and G. Barnes. 2000. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 12:63-71). Targeting and capture of MT plus ends at the cell periphery has been described, but whether or not the minus ends of these MTs are anchored at the centrosome is not known. Here, we show that release of short MTs from the centrosome is frequent in migrating cells and that their transport toward the cell periphery is blocked when dynein activity is impaired. We further show that MT release, but not MT nucleation or polymerization dynamics, is abolished by overexpression of the centrosomal MT-anchoring protein ninein. In addition, a dramatic inhibition of cell migration was observed; but, contrary to cells treated by drugs inhibiting MT dynamics, polarized membrane ruffling activity was not affected in ninein overexpressing cells. We thus propose that the balance between MT minus-end capture and release from the centrosome is critical for efficient cell migration.
Figures
References
-
- Fukata, M., T. Watanabe, J. Noritake, M. Nakagawa, M. Yamaga, S. Kuroda, Y. Mutsuura, A. Iwamatsu, F. Perez, and K. Kaibuchi. 2002. Rac 1 and Cdc 42 capture microtubules through IQGAP1 and CLIP-170. Cell. 109:873–885. - PubMed
-
- Garces, J.A., I.B. Clark, D.I. Meyer, and R.B. Vallee. 1999. Interaction of the p62 subunit of dynactin with Arp1 and the cortical actin cytoskeleton. Curr. Biol. 9:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Goode, B.L., D.G. Drubin, and G. Barnes. 2000. Functional cooperation between the microtubule and actin cytoskeletons. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:63–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

