A locus for migraine without aura maps on chromosome 14q21.2-q22.3
- PMID: 12474141
- PMCID: PMC378621
- DOI: 10.1086/345298
A locus for migraine without aura maps on chromosome 14q21.2-q22.3
Abstract
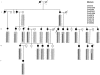
Migraine is a common and disabling neurological disease of unknown origin characterized by a remarkable clinical variability. It shows strong familial aggregation, suggesting that genetic factors are involved in its pathogenesis. Different approaches have been used to elucidate this hereditary component, but a unique transmission model and causative gene(s) have not yet been identified. We report clinical and molecular data from a large Italian pedigree in which migraine without aura (MO) segregates as an autosomal dominant trait. After exclusion of any association between MO and the known familial hemiplegic migraine and migraine with aura loci, we performed a genomewide linkage analysis using 482 polymorphic microsatellite markers. We obtained significant evidence of linkage between the MO phenotype and the marker D14S978 on 14q22.1 (maximum two-point LOD score of 3.70, at a recombination fraction of 0.01). Multipoint parametric analysis (maximum LOD score of 5.25 between markers D14S976 and D14S978) and haplotype construction showed strong evidence of linkage in a region of 10 cM flanked by markers D14S1027 and D14S980 on chromosome 14q21.2-q22.3. These results indicate the first evidence of a genetic locus associated with MO on chromosome 14.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Genetic Location Database, http://cedar.genetics.soton.ac.uk/public_html/ldb.html (for genetic-linkage distances)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for migraine [MIM 157300], FHM1 [MIM 141500], CACNA1A [MIM 601011], FHM2 [MIM 602481], MFTS [MIM 300125], MGAU [MIM 300125], GCH1 [MIM 600225], SPG3A [MIM 606439], PTGDR [MIM 606687], PTGER2 [MIM 176804], and BMP4 [MIM 112262])
-
- UCSC Human Genome Project Working Draft, http://genome.ucsc.edu/ (for choosing the microsatellite markers on chromosome 14q)
References
-
- Ai X, Cappuzzello J, Hall AK (1999) Activin and bone morphogenetic proteins induce calcitonin gene-related peptide in embryonic sensory neurons in vitro. Mol Cell Neurosci 14:506–518 - PubMed
-
- Curtis D, Gurling H (1993) A procedure for combining two-point lod scores into a summary multipoint map. Hum Hered 43:173–185 - PubMed
-
- Del Zompo M, Cherchi A, Palmas MA, Ponti M, Bocchetta A, Gessa GL, Piccardi MP (1998) Association between dopamine receptor genes and migraine without aura in a Sardinian sample. Neurology 51:781–786 - PubMed
-
- Ducros A, Denier C, Joutel A, Cecillon M, Lescoat C, Vahedi K, Dracel F, Vicaut E, Bousser MG, Tournier-Lasserve E (2001) The clinical spectrum of familial hemiplegic migraine associated with mutations in a neuronal calcium channel. N Engl J Med 345:17–24 - PubMed
-
- Ducros A, Joutel A, Vahedi K, Cecillon M, Ferreira A, Bernard E, Verier A, Echenne B, Lopez de Manain A, Bousser MG, Tournier-Lasserve E (1997) Mapping of a second locus for familial hemiplegic migraine to 1q21–23 and evidence of further heterogeneity. Ann Neurol 42:885–890 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

