A susceptibility gene for psoriatic arthritis maps to chromosome 16q: evidence for imprinting
- PMID: 12474146
- PMCID: PMC378616
- DOI: 10.1086/345646
A susceptibility gene for psoriatic arthritis maps to chromosome 16q: evidence for imprinting
Abstract
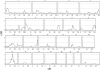
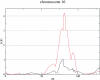
Several genetic loci have been reported for psoriasis, but none has been specifically linked to psoriatic arthritis (PsA), a condition that affects >10% of patients with psoriasis. A genetic component for PsA is suggested by segregation within families and high concordance among identical twins. We performed a linkage scan to map genes contributing to PsA. We identified 178 patients with PsA out of 906 patients who were included in our genetic study of psoriasis. Using a comprehensive genealogy database, we were able to connect 100 of these into 39 families. We genotyped the patients using a framework marker set of 1,000 microsatellite markers, with an average density of 3 cM, and performed multipoint, affected-only, allele-sharing linkage analysis using the Allegro program. On the basis of the initial results, we genotyped more markers for the most prominent loci. A linkage with a LOD score of 2.17 was observed on chromosome 16q. The linkage analysis, conditioned on paternal transmission to affected individuals, gave a LOD score of 4.19, whereas a LOD score of only 1.03 was observed when conditioned for maternal transmission. A suggestive locus on chromosome 16q has previously been implicated in psoriasis. Our data indicate that a gene at this locus may be involved in paternal transmission of PsA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetics of psoriasis in Iceland: evidence for linkage of subphenotypes to distinct Loci.J Invest Dermatol. 2005 Jun;124(6):1177-85. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23703.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 15955092
-
A genomewide scan identifies two novel loci involved in specific language impairment.Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Feb;70(2):384-98. doi: 10.1086/338649. Epub 2002 Jan 4. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11791209 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide scan for linkage to chromosomal regions in 382 sibling pairs with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.Am J Psychiatry. 2002 May;159(5):803-12. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.5.803. Am J Psychiatry. 2002. PMID: 11986135
-
What have we learned about genetic susceptibility in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis?Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015 Jan;27(1):91-8. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000136. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25415529 Review.
-
Psoriasis: a complex clinical and genetic disorder.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2004 Aug;6(4):314-6. doi: 10.1007/s11926-004-0044-x. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15251084 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis from genetic studies.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Apr;43(2):221-234. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00843-2. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 33712923 Review.
-
Genetics, Epigenetics, and Gender Impact in Axial-Spondyloarthritis Susceptibility: An Update on Genetic Polymorphisms and Their Sex Related Associations.Front Genet. 2021 Aug 10;12:671976. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.671976. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34447407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etiopathogenesis of Psoriasis from Genetic Perspective: An updated Review.Curr Genomics. 2022 Jul 5;23(3):163-174. doi: 10.2174/1389202923666220527111037. Curr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36777004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Psoriatic arthritis : a permanent challenge for rheumatologists and patients--Part 1: epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical course].Z Rheumatol. 2011 Oct;70(8):685-97. doi: 10.1007/s00393-011-0860-0. Z Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21912984 Review. German.
-
What epidemiology has told us about risk factors and aetiopathogenesis in rheumatic diseases.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):223. doi: 10.1186/ar2585. Epub 2009 May 19. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19490599 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for psoriasis [MIM 177900] and NOD2 [MIM 605956])
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/
References
-
- Akolkar PN, Gulwani-Akolkar B, Heresbach D, Lin XY, Fisher S, Katz S, Silver J (1997) Differences in risk of Crohn's disease in offspring of mothers and fathers with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 92:2241–2244 - PubMed
-
- Alcolado JC, Laji K, Gill-Randall R (2002) Maternal transmission of diabetes. Diabet Med 19:89–98 - PubMed
-
- Al-Heresh AM, Proctor J, Jones SM, Dixey J, Cox B, Welsh K, McHugh N (2002) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha polymorphism and the HLA-Cw*0602 allele in psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology 41:525–530 - PubMed
-
- Baker BS, Swain AF, Fry L, Valdimarsson H (1984) Epidermal T lymphocytes and HLA-DR expression in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 110:555–564 - PubMed
-
- Balendran N, Clough RL, Arguello JR, Barber R, Veal C, Jones AB, Rosbotham JL, Little AM, Madrigal A, Barker JN, Powis SH, Trembath RC (1999) Characterization of the major susceptibility region for psoriasis at chromosome 6p21.3. J Invest Dermatol 113:322–328 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

