Cloning and characterization of scon-3+, a new member of the Neurospora crassa sulfur regulatory system
- PMID: 12477788
- PMCID: PMC138751
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.1.6.875-883.2002
Cloning and characterization of scon-3+, a new member of the Neurospora crassa sulfur regulatory system
Abstract
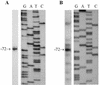
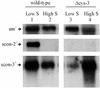
The sulfur regulatory system of Neurospora crassa consists of a group of sulfur-regulated structural genes (e.g., arylsulfatase) that are under coordinate control of the CYS3 positive regulator and sulfur controller (SCON) negative regulators. Here we report on the cloning of scon-3(+), which encodes a polypeptide of 171 amino acids and is a Skp1 family homolog. Repeat-induced point mutation of scon-3(+) resulted in a phenotype of constitutive expression of arylsulfatase, a phenotype consistent with other sulfur controller mutants. Northern analysis indicated that, unlike other members of the sulfur regulatory system, expression of scon-3(+) is not under the direct control of the CYS3 transcriptional activator. In particular, scon-3(+) mRNA was detectable under sulfur repressing or derepressing conditions in a Deltacys-3 mutant. In yeast, Skp1p and an F-box protein binding partner are core constituents of a class of E3 ubiquitin ligases known as SCF complexes. The N. crassa negative regulator SCON2 contains an F-box motif essential for the operation of the sulfur regulatory system and suggests a role for an SCF complex in the N. crassa sulfur regulatory system. A crucial set of experiments, by using a yeast two-hybrid approach with confirming coimmunoprecipitation assays, demonstrated that SCON3 interacts with SCON2 in a manner dependent upon the F-box motif of SCON2. The protein-protein interaction detected between SCON2 and SCON3 represents the initial demonstration in a filamentous fungus of functional interaction between putative core components of a SCF complex.
Figures




References
-
- Bai, C., P. Sen, K. Hofmann, L. Ma, M. Goebl, J. W. Harper, and S. J. Elledge. 1996. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell 86:263-274. - PubMed
-
- Bartel, P. L., C.-T. Chien, R. Sternglanz, and S. Fields. 1993. Using the two-hybrid system to detect protein-protein interactions, p. 153-179. In D. A. Hartley (ed.), Cellular interactions in development: a practical approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, England.
-
- Bruchez, J. J. P., J. Eberle, and V. E. A. Russo. 1993. Regulatory sequences in the transcription of Neurospora crassa genes: CAAT box, TATA box, introns, poly(A) tail formation sequences. Fung. Genet. Newsl. 40:89-96.
-
- Cambareri, E. B., H. M. Foss, M. R. Rountree, and E. U. Selker. 1989. Repeat induced G-C and A-T mutations in Neurospora. Science 244:1571-1575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

