Reduced sodium channel density, altered voltage dependence of inactivation, and increased susceptibility to seizures in mice lacking sodium channel beta 2-subunits
- PMID: 12481039
- PMCID: PMC139271
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.212638099
Reduced sodium channel density, altered voltage dependence of inactivation, and increased susceptibility to seizures in mice lacking sodium channel beta 2-subunits
Abstract
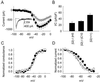
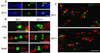
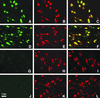
Sodium channel beta-subunits modulate channel gating, assembly, and cell surface expression in heterologous cell systems. We generated beta2(-/-) mice to investigate the role of beta2 in control of sodium channel density, localization, and function in neurons in vivo. Measurements of [(3)H]saxitoxin (STX) binding showed a significant reduction in the level of plasma membrane sodium channels in beta2(-/-) neurons. The loss of beta2 resulted in negative shifts in the voltage dependence of inactivation as well as significant decreases in sodium current density in acutely dissociated hippocampal neurons. The integral of the compound action potential in optic nerve was significantly reduced, and the threshold for action potential generation was increased, indicating a reduction in the level of functional plasma membrane sodium channels. In contrast, the conduction velocity, the number and size of axons in the optic nerve, and the specific localization of Na(v)1.6 channels in the nodes of Ranvier were unchanged. beta2(-/-) mice displayed increased susceptibility to seizures, as indicated by reduced latency and threshold for pilocarpine-induced seizures, but seemed normal in other neurological tests. Our observations show that beta2-subunits play an important role in the regulation of sodium channel density and function in neurons in vivo and are required for normal action potential generation and control of excitability.
Figures



References
-
- Catterall W. A. (2000) Neuron 26, 13-25. - PubMed
-
- Goldin A. L. (1993) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 3, 272-277. - PubMed
-
- Isom L. L., De Jongh, K. S. & Catterall, W. A. (1994) Neuron 12, 1183-1194. - PubMed
-
- Isom L. L. (2000) Am. J. Physiol. 278, G349-G353. - PubMed
-
- Malhotra J. D., Kazen-Gillespie, K., Hortsch, M. & Isom, L. L. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 11383-11388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5P30CA46592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS25704/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH019547/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039479/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30DK34933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017965/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS17965/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HD07505-03/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007505/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RG-2882-A-1/RG/CSR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS025704/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32 MH 19547/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 3P60DK20572-22S2/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059980/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS39479/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

