Activation of a PTX-insensitive G protein is involved in histamine-induced recombinant M-channel modulation
- PMID: 12482885
- PMCID: PMC2290715
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.026583
Activation of a PTX-insensitive G protein is involved in histamine-induced recombinant M-channel modulation
Abstract
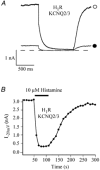
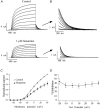
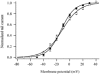
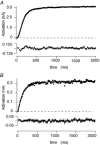
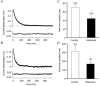
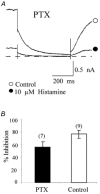
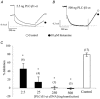
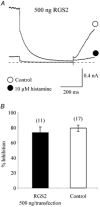
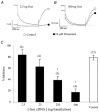
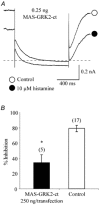
The M-type potassium current (I(M)) plays a dominant role in regulating membrane excitability and is modulated by many neurotransmitters. However, except in the case of bradykinin, the signal transduction pathways involved in M-channel modulation have not been fully elucidated. The channels underlying I(M) are produced by the coassembly of KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 channel subunits and can be expressed in heterologous systems where they can be modulated by several neurotransmitter receptors including histamine H(1) receptors. In HEK293T cells, histamine acting via transiently expressed H(1)R produced a strong inhibition of recombinant M-channels but had no overt effects on the voltage dependence or voltage range of I(M) activation. In addition, the modulation of I(M) by histamine was not voltage sensitive, whereas channel gating, particularly deactivation, was accelerated by histamine. Non-hydrolysable guanine nucleotide analogues (GDP-beta-S and GTP-gamma-S) and pertussis toxin (PTX) treatment demonstrated the involvement of a PTX-insensitive G protein in the signal transduction pathway mediating histamine-induced I(M) modulation. Abrogation of the histamine-induced modulation of I(M) by expression of a C-terminal construct of phospholipase C (PLC-beta1-ct), which buffers activated Galpha(q/11) subunits, implicates this G protein alpha subunit in the modulatory pathway. On the other hand, abrogation of the histamine-induced modulation of I(M) by expression of two constructs which buffer free betagamma subunits, transducin (Galphat) and a C-terminal construct of a G protein receptor kinase (MAS-GRK2-ct), implicates betagamma dimers in the modulatory pathway. These findings demonstrate that histamine modulates recombinant M-channels in HEK293T cells via a PTX-insensitive G protein, probably Galpha(q/11), in a similar manner to a number of other G protein-coupled receptors. However, histamine-induced I(M) modulation in HEK293T cells is novel in that betagamma subunits in addition to Galpha(q/11) subunits appear to be involved in the modulation of KCNQ2/3 channel currents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Histamine inhibits KCNQ2/KCNQ3 channel current via recombinant histamine H(1) receptors.Neurosci Lett. 2002 Aug 16;328(3):285-8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(02)00484-6. Neurosci Lett. 2002. PMID: 12147327
-
Activation of muscarinic m5 receptors inhibits recombinant KCNQ2/KCNQ3 K+ channels expressed in HEK293T cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Feb 21;462(1-3):25-32. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01323-2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12591092
-
A voltage-independent calcium current inhibitory pathway activated by muscarinic agonists in rat sympathetic neurons requires both Galpha q/11 and Gbeta gamma.J Neurosci. 2000 Aug 1;20(15):5623-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-15-05623.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10908599 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of ion channels by somatostatin and acetylcholine.Prog Neurobiol. 1992;38(2):203-30. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(92)90040-l. Prog Neurobiol. 1992. PMID: 1372125 Review.
-
Ion-channel regulation by G proteins.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001 Nov;12(9):391-8. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(01)00475-1. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001. PMID: 11595540 Review.
Cited by
-
The cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 inhibits transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) and evokes peripheral antihyperalgesia via calcineurin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 25;103(30):11393-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603861103. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16849427 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin 5-HT2C receptor-mediated inhibition of the M-current in hypothalamic POMC neurons.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):E1399-406. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00565.2011. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22436698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown BS, Yu SP. Modulation and genetic identification of the M channel. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. 2000;73:135–166. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA. M currents. Ion Channels. 1988;1:55–94. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Adams PR. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1980;283:673–676. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

