O2-sensitive K+ channels in immortalised rat chromaffin-cell-derived MAH cells
- PMID: 12482887
- PMCID: PMC2290717
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.028415
O2-sensitive K+ channels in immortalised rat chromaffin-cell-derived MAH cells
Abstract
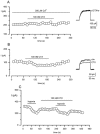
The regulation of K(+) channels by O(2) levels is a key link between hypoxia and neurotransmitter release in neuroendocrine cells. Here, we examined the effects of hypoxia on K(+) channels in the immortalised v-myc, adrenal-derived HNK1(+) (MAH) cell line. MAH cells possess a K(+) conductance that is sensitive to Cd(2+), iberiotoxin and apamin, and which is inhibited by ~24 % when exposed to a hypoxic perfusate (O(2) tension 20 mmHg). This conductance was attributed to high-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK) and small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (SK) channels, which are major contributors to the O(2)-sensitive K(+) conductance in adrenomedullary chromaffin cells. Under low [Ca(2+)](i) conditions that prevented activation of Ca(2+)-dependent K(+) conductances, a rapidly activating and slowly inactivating K(+) conductance, sensitive to both TEA and 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), but insensitive to 100 nM charybdotoxin (CTX), was identified. This current was also reduced (by ~25 %) when exposed to hypoxia. The hypoxia-sensitive component of this current was greatly attenuated by 10 mM 4-AP, but was only slightly reduced by 10 mM TEA. This suggests the presence of delayed-rectifier O(2)-sensitive channels comprising homomultimeric Kv1.5 or heteromultimeric Kv1.5/Kv1.2 channel subunits. The presence of both Kv1.5 and Kv1.2 alpha-subunits was confirmed using immunocytochemical techniques. We also demonstrated that these K(+) channel subunits are present in neonatal rat adrenomedullary chromaffin cells in situ. These data indicate that MAH cells possess O(2)-sensitive K(+) channels with characteristics similar to those observed previously in isolated chromaffin cells, and therefore provide an excellent model for examining the cellular mechanisms of O(2) sensing in adrenomedullary chromaffin cells.
Figures







References
-
- Beitner-Johnson D, Shull GE, Dedman JR, Millhorn DE. Regulation of gene expression by hypoxia: a molecular approach. Respiration Physiology. 1997;110:87–97. - PubMed
-
- Birren SJ, Anderson DJ. A v-myc-immortalized sympathoadrenal progenitor cell line in which neuronal differentiation is initiated by FGF but not NGF. Neuron. 1990;4:189–201. - PubMed
-
- Blatz AL, Magleby KL. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986;323:718–720. - PubMed
-
- Campbell AGM, Dawes GS, Fishman AP. Regional distribution of blood flow in the mature fetal lamb. Circulation Research. 1967;21:229–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

