Leptin inhibits epileptiform-like activity in rat hippocampal neurones via PI 3-kinase-driven activation of BK channels
- PMID: 12482897
- PMCID: PMC2290718
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.029488
Leptin inhibits epileptiform-like activity in rat hippocampal neurones via PI 3-kinase-driven activation of BK channels
Abstract
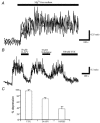
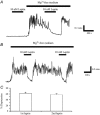
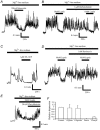
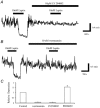
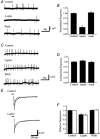
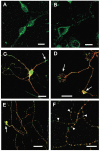
The obese gene product, leptin is an important circulating satiety factor that regulates energy balance via its actions in the hypothalamus. However, leptin receptors are also expressed in brain regions not directly associated with energy homeostasis, such as the hippocampus. Here, leptin inhibits hippocampal neurones via activation of large conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK) channels, a process that may be important in regulating neuronal excitability. We now show that leptin receptor labelling is expressed on somata, dendrites and axons, and is also concentrated at synapses in hippocampal cultures. In functional studies, leptin potently and reversibly reduces epileptiform-like activity evoked in lean, but not leptin-resistant Zucker fa/fa rats. Furthermore, leptin also depresses enhanced Ca(2+) levels evoked following Mg(2+) removal in hippocampal cultures. The ability of leptin to modulate this activity requires activation of BK, but not K(ATP), channels as the effects of leptin were mimicked by the BK channel activator NS-1619, and inhibited by the BK channel inhibitors, iberiotoxin and charybdotoxin. The signalling mechanisms underlying this process involve stimulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase), but not mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), as two structurally unrelated inhibitors of PI 3-kinase, LY294002 and wortmannin, blocked the actions of leptin. These data indicate that leptin, via PI 3-kinase-driven activation of BK channels, elicits a novel mechanism for controlling neuronal excitability. As uncontrolled excitability in the hippocampus is one underlying cause of temporal lobe epilepsy, this novel action of leptin could provide an alternative therapeutic target in the management of epilepsy.
Figures
References
-
- Abele AE, Miller RJ. Potassium channel activators abolish excitotoxicity in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neuroscience Letters. 1990;115:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Abele AE, Scholz KP, Scholz WK, Miller RJ. Excitotoxicity induced by enhanced neurotransmission in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neuron. 1990;4:413–419. - PubMed
-
- Ahima RS, Flier JS. Leptin. Annual Review Physiology. 2000;62:413–437. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Cuendo A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 98059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

