The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade functions in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
- PMID: 12482967
- PMCID: PMC140665
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.1.131-139.2003
The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade functions in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
Abstract
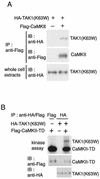
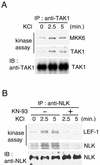
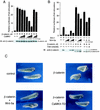
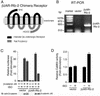
Wnt signaling controls a variety of developmental processes. The canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway functions to stabilize beta-catenin, and the noncanonical Wnt/Ca(2+) pathway activates Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). In addition, the Wnt/Ca(2+) pathway activated by Wnt-5a antagonizes the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway via an unknown mechanism. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway composed of TAK1 MAPK kinase kinase and NLK MAPK also negatively regulates the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Here we show that activation of CaMKII induces stimulation of the TAK1-NLK pathway. Overexpression of Wnt-5a in HEK293 cells activates NLK through TAK1. Furthermore, by using a chimeric receptor (beta(2)AR-Rfz-2) containing the ligand-binding and transmembrane segments from the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor (beta(2)AR) and the cytoplasmic domains from rat Frizzled-2 (Rfz-2), stimulation with the beta-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol activates activities of endogenous CaMKII, TAK1, and NLK and inhibits beta-catenin-induced transcriptional activation. These results suggest that the TAK1-NLK MAPK cascade is activated by the noncanonical Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway and antagonizes canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The TAK1-NLK-MAPK-related pathway antagonizes signalling between beta-catenin and transcription factor TCF.Nature. 1999 Jun 24;399(6738):798-802. doi: 10.1038/21674. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10391247
-
Regulation of lymphoid enhancer factor 1/T-cell factor by mitogen-activated protein kinase-related Nemo-like kinase-dependent phosphorylation in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;23(4):1379-89. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1379-1389.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12556497 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt activates the Tak1/Nemo-like kinase pathway.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):17232-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307801200. Epub 2004 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14960582
-
New steps in the Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction pathway.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000;55:225-36. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000. PMID: 11036939 Review.
-
Noncanonical Wnt signaling in vertebrate development, stem cells, and diseases.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010 Dec;90(4):243-56. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20195. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010. PMID: 21181886 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein acetylation and deacetylation: An important regulatory modification in gene transcription (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2020 Oct;20(4):2923-2940. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9073. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32855658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Burden of rare deleterious variants in WNT signaling genes among 511 myelomeningocele patients.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 24;15(9):e0239083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239083. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32970752 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling between osteoblast-lineage cells and osteoclast precursors enhances osteoclastogenesis.Nat Med. 2012 Feb 19;18(3):405-12. doi: 10.1038/nm.2653. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22344299
-
The mechanism of endogenous receptor activation functionally distinguishes prototype canonical and noncanonical Wnts.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 May;25(9):3475-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.9.3475-3482.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15831454 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a regulates distinct signalling pathways by binding to Frizzled2.EMBO J. 2010 Jan 6;29(1):41-54. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.322. Epub 2009 Nov 12. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 19910923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behrens, J., J. P. von Kries, M. Kuhl, L. Bruhn, D. Wedlich, R. Grosschedl, and W. Birchmeier. 1996. Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382:638-642. - PubMed
-
- Cardigan, K. M., and R. Nusse. 1997. Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11:3286-3305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
