Proteolytic cleavage of MLL generates a complex of N- and C-terminal fragments that confers protein stability and subnuclear localization
- PMID: 12482972
- PMCID: PMC140678
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.1.186-194.2003
Proteolytic cleavage of MLL generates a complex of N- and C-terminal fragments that confers protein stability and subnuclear localization
Abstract
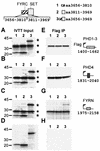
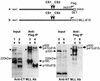
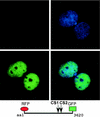
The mixed-lineage leukemia gene (MLL, ALL1, HRX) encodes a 3,969-amino-acid nuclear protein homologous to Drosophila trithorax and is required to maintain proper Hox gene expression. Chromosome translocations in human leukemia disrupt MLL (11q23), generating chimeric proteins between the N terminus of MLL and multiple translocation partners. Here we report that MLL is normally cleaved at two conserved sites (D/GADD and D/GVDD) and that mutation of these sites abolishes the proteolysis. MLL cleavage generates N-terminal p320 (N320) and C-terminal p180 (C180) fragments, which form a stable complex that localizes to a subnuclear compartment. The FYRN domain of N320 directly interacts with the FYRC and SET domains of C180. Disrupting the interaction between N320 and C180 leads to a marked decrease in the level of N320 and a redistribution of C180 to a diffuse nuclear pattern. These data suggest a model in which a dynamic post-cleavage association confers stability to N320 and correct nuclear sublocalization of the complex, to control the availability of N320 for target genes. This predicts that MLL fusion proteins of leukemia which would lose the ability to complex with C180 have their stability conferred instead by the fusion partners, thus providing one mechanism for altered target gene expression.
Figures





References
-
- Armstrong, S. A., J. E. Staunton, L. B. Silverman, R. Pieters, M. L. den Boer, M. D. Minden, S. E. Sallan, E. S. Lander, T. R. Golub, and S. J. Korsmeyer. 2002. MLL translocations specify a distinct gene expression profile that distinguishes a unique leukemia. Nat. Genet. 30:41-47. - PubMed
-
- Ayton, P. M., and M. L. Cleary. 2001. Molecular mechanisms of leukemogenesis mediated by MLL fusion proteins. Oncogene 20:5695-5707. - PubMed
-
- Breen, T. R., and P. J. Harte. 1993. Trithorax regulates multiple homeotic genes in the bithorax and Antennapedia complexes and exerts different tissue-specific, parasegment-specific and promoter-specific effects on each. Development 117:119-134. - PubMed
-
- Butler, L. H., R. Slany, X. Cui, M. L. Cleary, and D. Y. Mason. 1997. The HRX proto-oncogene product is widely expressed in human tissues and localizes to nuclear structures. Blood 89:3361-3370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
