Two different Drosophila ADA2 homologues are present in distinct GCN5 histone acetyltransferase-containing complexes
- PMID: 12482983
- PMCID: PMC140672
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.1.306-321.2003
Two different Drosophila ADA2 homologues are present in distinct GCN5 histone acetyltransferase-containing complexes
Abstract
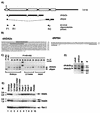
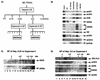
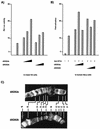
We have isolated a novel Drosophila (d) gene coding for two distinct proteins via alternative splicing: a homologue of the yeast adaptor protein ADA2, dADA2a, and a subunit of RNA polymerase II (Pol II), dRPB4. Moreover, we have identified another gene in the Drosophila genome encoding a second ADA2 homologue (dADA2b). The two dADA2 homologues, as well as many putative ADA2 homologues from different species, all contain, in addition to the ZZ and SANT domains, several evolutionarily conserved domains. The dada2a/rpb4 and dada2b genes are differentially expressed at various stages of Drosophila development. Both dADA2a and dADA2b interacted with the GCN5 histone acetyltransferase (HAT) in a yeast two-hybrid assay, and dADA2b, but not dADA2a, also interacted with Drosophila ADA3. Both dADA2s further potentiate transcriptional activation in insect and mammalian cells. Antibodies raised either against dADA2a or dADA2b both immunoprecipitated GCN5 as well as several Drosophila TATA binding protein-associated factors (TAFs). Moreover, following glycerol gradient sedimentation or chromatographic purification combined with gel filtration of Drosophila nuclear extracts, dADA2a and dGCN5 were detected in fractions with an apparent molecular mass of about 0.8 MDa whereas dADA2b was found in fractions corresponding to masses of at least 2 MDa, together with GCN5 and several Drosophila TAFs. Furthermore, in vivo the two dADA2 proteins showed different localizations on polytene X chromosomes. These results, taken together, suggest that the two Drosophila ADA2 homologues are present in distinct GCN5-containing HAT complexes.
Figures




References
-
- Aasland, R., A. F. Stewart, and T. Gibson. 1996. The SANT domain: a putative DNA-binding domain in the SWI-SNF and ADA complexes, the transcriptional co-repressor N-CoR and TFIIIB. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21:87-88. - PubMed
-
- Balaguer, P., A. M. Boussioux, E. Demirpence, and J. C. Nicolas. 2001. Reporter cell lines are useful tools for monitoring biological activity of nuclear receptor ligands. Luminescence 16:153-158. - PubMed
-
- Barlev, N. A., R. Candau, L. Wang, P. Darpino, N. Silverman, and S. L. Berger. 1995. Characterization of physical interactions of the putative transcriptional adaptor, ADA2, with acidic activation domains and TATA-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 270:19337-19344. - PubMed
-
- Belenkaya, T., A. Soldatov, E. Nabirochkina, I. Birjukova, S. Georgieva, and P. Georgiey. 1998. P-element insertion at the polyhomeotic gene leads to formation of a novel chimeric protein that negatively regulates yellow gene expression in P-element-induced alleles of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 150:687-697. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
