An Arabidopsis SET domain protein required for maintenance but not establishment of DNA methylation
- PMID: 12486005
- PMCID: PMC139107
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf687
An Arabidopsis SET domain protein required for maintenance but not establishment of DNA methylation
Abstract
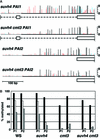
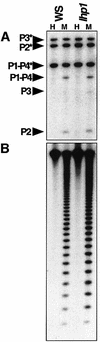
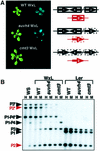
Cytosine methylation is critical for correct development and genome stability in mammals and plants. In order to elucidate the factors that control genomic DNA methylation patterning, a genetic screen for mutations that disrupt methylation-correlated silencing of the endogenous gene PAI2 was conducted in Arabidopsis: This screen yielded seven loss-of-function alleles in a SET domain protein with histone H3 Lys9 methyltransferase activity, SUVH4. The mutations conferred reduced cytosine methylation on PAI2, especially in non-CG sequence contexts, but did not affect methylation on another PAI locus carrying two genes arranged as an inverted repeat. Moreover, an unmethylated PAI2 gene could be methylated de novo in the suvh4 mutant background. These results suggest that SUVH4 is involved in maintenance but not establishment of methylation at particular genomic regions. In contrast, a heterochromatin protein 1 homolog, LHP1, had no effect on PAI methylation.
Figures
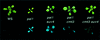



References
-
- Baumbusch L.O., Thorstensen,T., Krauss,V., Fischer,A., Naumann,K., Assalkhou,R., Schulz,I., Reuter,G. and Aalen,R.B. (2001) The Arabidopsis thaliana genome contains at least 29 active genes encoding SET domain proteins that can be assigned to four evolutionarily conserved classes. Nucleic Acids Res., 29, 4319–4333. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bell C.J. and Ecker,J.R. (1994) Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics, 19, 137–144. - PubMed
-
- Bender J. (2001) A vicious cycle: RNA silencing and DNA methylation in plants. Cell, 106, 129–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

