Forespore-specific expression of Bacillus subtilis yqfS, which encodes type IV apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease, a component of the base excision repair pathway
- PMID: 12486072
- PMCID: PMC141825
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.1.340-348.2003
Forespore-specific expression of Bacillus subtilis yqfS, which encodes type IV apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease, a component of the base excision repair pathway
Abstract
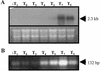
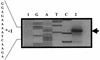
The temporal and spatial expression of the yqfS gene of Bacillus subtilis, which encodes a type IV apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease, was studied. A reporter gene fusion to the yqfS opening reading frame revealed that this gene is not transcribed during vegetative growth but is transcribed during the last steps of the sporulation process and is localized to the developing forespore compartment. In agreement with these results, yqfS mRNAs were mainly detected by both Northern blotting and reverse transcription-PCR, during the last steps of sporulation. The expression pattern of the yqfS-lacZ fusion suggested that yqfS may be an additional member of the Esigma(G) regulon. A primer extension product mapped the transcriptional start site of yqfS, 54 to 55 bp upstream of translation start codon of yqfS. Such an extension product was obtained from RNA samples of sporulating cells but not from those of vegetatively growing cells. Inspection of the nucleotide sequence lying upstream of the in vivo-mapped transcriptional yqfS start site revealed the presence of a sequence with good homology to promoters preceding genes of the sigma(G) regulon. Although yqfS expression was temporally regulated, neither oxidative damage (after either treatment with paraquat or hydrogen peroxide) nor mitomycin C treatment induced the transcription of this gene.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The ytkD (mutTA) gene of Bacillus subtilis encodes a functional antimutator 8-Oxo-(dGTP/GTP)ase and is under dual control of sigma A and sigma F RNA polymerases.J Bacteriol. 2004 Feb;186(4):1050-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.4.1050-1059.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 14761999 Free PMC article.
-
YqfS from Bacillus subtilis is a spore protein and a new functional member of the type IV apurinic/apyrimidinic-endonuclease family.J Bacteriol. 2003 Sep;185(18):5380-90. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.18.5380-5390.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12949090 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal regulation and forespore-specific expression of the spore photoproduct lyase gene by sigma-G RNA polymerase during Bacillus subtilis sporulation.J Bacteriol. 1994 Jul;176(13):3983-91. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.13.3983-3991.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 8021181 Free PMC article.
-
Compartmentalized gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.Trends Genet. 1991 May;7(5):167-72. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90381-y. Trends Genet. 1991. PMID: 1906210 Review.
-
Expression of stage II genes during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.Res Microbiol. 1991 Sep-Oct;142(7-8):841-5. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90063-g. Res Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 1784821 Review.
Cited by
-
The ytkD (mutTA) gene of Bacillus subtilis encodes a functional antimutator 8-Oxo-(dGTP/GTP)ase and is under dual control of sigma A and sigma F RNA polymerases.J Bacteriol. 2004 Feb;186(4):1050-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.4.1050-1059.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 14761999 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Nfo and ExoA apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases in radiation resistance and radiation-induced mutagenesis of Bacillus subtilis spores.J Bacteriol. 2011 Jun;193(11):2875-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00134-11. Epub 2011 Mar 25. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21441501 Free PMC article.
-
YqfS from Bacillus subtilis is a spore protein and a new functional member of the type IV apurinic/apyrimidinic-endonuclease family.J Bacteriol. 2003 Sep;185(18):5380-90. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.18.5380-5390.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12949090 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of transcriptional terminators in Bacillus subtilis and related species.PLoS Comput Biol. 2005 Aug;1(3):e25. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010025. Epub 2005 Aug 12. PLoS Comput Biol. 2005. PMID: 16110342 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient processing of abasic sites by bacterial nonhomologous end-joining Ku proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 1;42(21):13082-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1029. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25355514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barzilay, G., and L. D. Hickson. 1995. Structure and function of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. Bioessays 17:713-719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

