Choline starvation induces the gene licD2 in Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 12486075
- PMCID: PMC141818
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.1.371-373.2003
Choline starvation induces the gene licD2 in Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
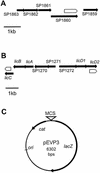
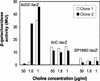
Mutant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae were constructed to monitor the regulation of three dispersed genes known or predicted to act in choline metabolism. One gene (licD2) was regulated in response to choline deprivation over a 30-fold range. The other two (SP1860 and licC) responded little if at all to the same challenge.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cellular localization of choline-utilization proteins in Streptococcus pneumoniae using novel fluorescent reporter systems.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Oct;74(2):395-408. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06872.x. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19737355
-
Pneumococcal licD2 gene is involved in phosphorylcholine metabolism.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Mar;31(5):1477-88. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01291.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10200966
-
Versatility of choline metabolism and choline-binding proteins in Streptococcus pneumoniae and commensal streptococci.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009 May;33(3):572-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00172.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19396958 Review.
-
Versatility of choline-binding domain.Microb Drug Resist. 1998 Spring;4(1):25-36. doi: 10.1089/mdr.1998.4.25. Microb Drug Resist. 1998. PMID: 9533722 Review. No abstract available.
-
Relationship between codon biased genes, microarray expression values and physiological characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae.Microbiology (Reading). 2004 Jul;150(Pt 7):2313-2325. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27097-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2004. PMID: 15256573
Cited by
-
Wind River Conference on Prokaryotic Biology--2002.J Bacteriol. 2003 Jan;185(1):7-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.1.7-12.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12486034 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Polysaccharide Capsule Composition of Pneumococcal Serotype 19A Subtypes Is Unaltered among Subtypes and Independent of the Nutritional Environment.Infect Immun. 2016 Oct 17;84(11):3152-3160. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00474-16. Print 2016 Nov. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27550933 Free PMC article.
-
The CiaRH system of Streptococcus pneumoniae prevents lysis during stress induced by treatment with cell wall inhibitors and by mutations in pbp2x involved in beta-lactam resistance.J Bacteriol. 2006 Mar;188(5):1959-68. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.5.1959-1968.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16484208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badger, E. 1944. The structural specificity of choline for the growth of type III pneumococcus. J. Biol. Chem. 31:183-191.
-
- Claverys, J. P., A. Dintilhac, E. V. Pestova, B. Martin, and D. A. Morrison. 1995. Construction and evaluation of new drug-resistance cassettes for gene disruption mutagenesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae, using an ami test platform. Gene 164:123-128. - PubMed
-
- Fischer, W. 1997. Pneumococcal lipoteichoic and teichoic acid. Microb. Drug Res. 3:309-325. - PubMed
-
- Fischer, W. 2000. Phosphocholine of pneumococcal teichoic acids: role in bacterial physiology and pneumococcal infection. Res. Microbiol. 151:421-427. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

