Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhaled antigen
- PMID: 12486107
- PMCID: PMC2196061
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021340
Lipopolysaccharide-enhanced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhaled antigen
Abstract
Allergic asthma is an inflammatory lung disease initiated and directed by T helper cells type 2 (Th2). The mechanism involved in generation of Th2 responses to inert inhaled antigens, however, is unknown. Epidemiological evidence suggests that exposure to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or other microbial products can influence the development and severity of asthma. However, the mechanism by which LPS influences asthma pathogenesis remains undefined. Although it is known that signaling through Toll-like receptors (TLR) is required for adaptive T helper cell type 1 (Th1) responses, it is unclear if TLRs are needed for Th2 priming. Here, we report that low level inhaled LPS signaling through TLR4 is necessary to induce Th2 responses to inhaled antigens in a mouse model of allergic sensitization. The mechanism by which LPS signaling results in Th2 sensitization involves the activation of antigen-containing dendritic cells. In contrast to low levels, inhalation of high levels of LPS with antigen results in Th1 responses. These studies suggest that the level of LPS exposure can determine the type of inflammatory response generated and provide a potential mechanistic explanation of epidemiological data on endotoxin exposure and asthma prevalence.
Figures
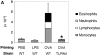
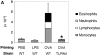
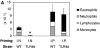
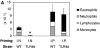
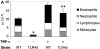
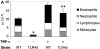
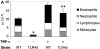
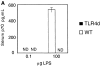

References
-
- Liu, A.H. 2002. Endotoxin exposure in allergy and asthma: reconciling a paradox. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 109:379–392. - PubMed
-
- Gern, J.E. 2000. Viral and bacterial infections in the development and progression of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 105:S497–S502. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov, R. 2001. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 1:135–145. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz, D.A. 2001. Does inhalation of endotoxin cause asthma? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 163:305–306. - PubMed
-
- Braun-Fahrlander, C., J. Riedler, U. Herz, W. Eder, M. Waser, L. Grize, S. Maisch, D. Carr, F. Gerlach, A. Bufe, et al. 2002. Environmental exposure to endotoxin and its relation to asthma in school-age children. N. Engl. J. Med. 347:869–877. - PubMed

