Modulation of serotonin 2C receptor editing by sustained changes in serotonergic neurotransmission
- PMID: 12486144
- PMCID: PMC6758441
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10529.2002
Modulation of serotonin 2C receptor editing by sustained changes in serotonergic neurotransmission
Abstract
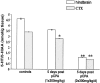
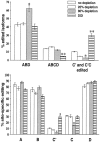
Serotonin 2C (5-HT2C) receptor pre-mRNA is a substrate for RNA editing enzymes that convert five adenosines (named A, B, C', C, and D editing sites) to inosines. Editing of two of these sites (C' and C) is crucial for decreasing the efficiency of the receptor to activate G-protein. Nucleotide sequence analysis of mouse forebrain neocortical 5-HT2C mRNA isoforms revealed that editing at these two sites is regulated in a serotonin-dependent manner. In serotonin-depleted mice, C'- and C-site editing is significantly decreased. This results in an increased expression of 5-HT2C mRNA isoforms encoding receptors with higher sensitivity to serotonin. In contrast, a 4 d treatment with the 5-HT2A/2C agonist (+/-)-1-(4-iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane significantly increases the editing frequency at the C' site and leads to increased expression of 5-HT2C mRNA isoforms encoding receptors that activate G-protein least efficiently. None of the drug treatments led to alterations in cytoplasmic 5-HT2C mRNA levels. These data indicate that editing of 5-HT2C pre-mRNA is a mechanism that retains basic response properties of 5-HT2C receptors in the face of changing synaptic input to keep receptor activation within an optimal range for information processing. Key words: serotonin; 5.
Figures

References
-
- Burns C, Chu H, Rueter S, Hutchinson LK, Canton H, Sanders-Bush E, Emeson RB. Regulation of serotonin-2C receptor G-protein coupling by RNA editing. Nature. 1997;387:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Gurevich I, Tamir H, Arango V, Dwork A, Mann JJ, Schmauss C. Altered editing of serotonin 2C receptor pre-mRNA in the prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide victims. Neuron. 2002;43:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Mann JJ, Huang Y-Y, Underwood MD, Kassir SA, Oppenheim S, Kelly TM, Dwork AJ, Arango V. A serotonin transporter gene promotor polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) and prefrontal cortical binding in major depression and suicide. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:729–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
