Alpha 4 integrins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 play a role in sympathetic innervation of the heart
- PMID: 12486170
- PMCID: PMC6758413
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10772.2002
Alpha 4 integrins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 play a role in sympathetic innervation of the heart
Abstract
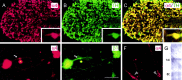
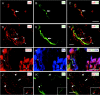
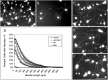
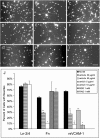
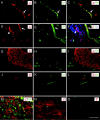
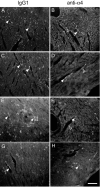
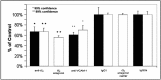
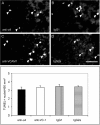
Sympathetic neurons innervate the heart early in postnatal development, an event that is crucial for proper modulation of blood pressure and cardiac function. However, the axon guidance cues that direct sympathetic neurons to the heart, and the neuronal receptors that recognize those cues, are poorly understood. Here we present evidence that interactions between the alpha4beta1 integrin on sympathetic neurons and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in the heart plays a role in cardiac innervation. The alpha4 subunit was detected on postnatal rat superior cervical ganglion (SCG) neurons in culture and in cryosections of SCG and heart. VCAM-1 immunoreactivity was detected on cardiac myocytes that associate with invading sympathetic neurons. Purified recombinant soluble VCAM-1 (rsVCAM-1) stimulated SCG neurite outgrowth at levels comparable with laminin 2/4 and fibronectin (Fn), and outgrowth on rs-VCAM-1 and Fn was blocked by antibodies specific for the alpha4 and beta1 integrin subunits. Intrathoracic injection of function-blocking antibodies to alpha4 and VCAM-1, as well as a small molecule inhibitor of alpha4 integrins, significantly reduced sympathetic innervation of the heart. These results indicate that the interaction between alpha4 integrin and VCAM-1 is important for sympathetic innervation of the heart.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and function of integrin alpha4beta1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) during sympathetic innervation of the heart.Dev Dyn. 2004 Oct;231(2):359-69. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20120. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 15366013
-
Involvement of alpha4 integrins in maintenance of cardiac sympathetic axons.Auton Neurosci. 2005 Oct 30;122(1-2):58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2005.08.006. Epub 2005 Sep 19. Auton Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16181811
-
Integrin alpha4beta1 (VLA-4) expression and activity in retinal and peripheral neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003 Jul;23(3):427-39. doi: 10.1016/s1044-7431(03)00065-4. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12837626
-
Immunosuppression by blocking alpha 4-integrins/VCAM-1 adhesion.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998;231:85-98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71987-5_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9479862 Review. No abstract available.
-
Anti-alpha4 integrin therapy for multiple sclerosis: mechanisms and rationale.Neurology. 2005 Apr 26;64(8):1336-42. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000158329.30470.D0. Neurology. 2005. PMID: 15851719 Review.
Cited by
-
Sympathetic neurons are a powerful driver of myocyte function in cardiovascular disease.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 14;6:38898. doi: 10.1038/srep38898. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27966588 Free PMC article.
-
Eph/ephrin interactions modulate vascular sympathetic innervation.Auton Neurosci. 2010 Dec 8;158(1-2):65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2010.06.004. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Auton Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20637710 Free PMC article.
-
The synaptic proteins neurexins and neuroligins are widely expressed in the vascular system and contribute to its functions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Dec 8;106(49):20782-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809510106. Epub 2009 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19926856 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF-A and Semaphorin3A: modulators of vascular sympathetic innervation.Dev Biol. 2009 Oct 1;334(1):119-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.07.023. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19631637 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing age alters the expression of the ryanodine receptor 3 isoform in adult rat superior cervical ganglia.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006 Aug;101(2):392-400. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00167.2006. Epub 2006 Apr 27. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006. PMID: 16645194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK, Juliano RL. Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:197–263. - PubMed
-
- Arroyo AG, Yang JT, Rayburn H, Hynes RO. Differential requirements for alpha4 integrins during fetal and adult hematopoiesis. Cell. 1996;85:997–1008. - PubMed
-
- Bayless KJ, Meininger GA, Scholtz JM, Davis GE. Osteopontin is a ligand for the alpha4beta1 integrin. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:1165–1174. - PubMed
-
- Berthoud HR, Powley TL. Interaction between parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves in prevertebral ganglia: morphological evidence for vagal efferent innervation of ganglion cells in the rat. Microsc Res Tech. 1996;35:80–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
